The Sciences
UFS study finds emerging pathogen inside brown locusts
Study Reveals Brown Locusts as Carriers of Pathogenic Yeasts Linked to Human Infections

A new study conducted by researchers from the University of the Free State (UFS), the National Health Laboratory Service, and the University of Venda has revealed for the first time that common brown locusts can carry pathogenic yeasts, including Candida auris, a fungus capable of causing severe infections in humans, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or those seriously ill.
The study, titled South African brown locusts, Locustana pardalina, hosts fluconazole-resistant, Candidozyma (Candida) auris (Clade III), uncovers the presence of the disease-causing yeast C. auris in the digestive tracts of locusts. This discovery highlights the potential for locusts to spread this emerging pathogen. The research began in April 2022, with 20 adult locusts collected during a significant locust outbreak in the semi-arid Eastern Karoo region of the Eastern Cape, which lasted from September 2021 to May 2022. The study is currently under peer review.
According to Prof. Carlien Pohl-Albertyn, National Research Foundation (NRF) SARChI Research Chair in Pathogenic Yeasts, the researchers isolated three strains of C. auris from different locusts, two of which also contained strains of Candida orthopsilosis, another potentially pathogenic yeast. “The fact that we were able to isolate C. auris from 15% of the sampled locusts, using non-selective media and a non-restrictive temperature of 30°C, may indicate that C. auris is abundant in the locusts and that specific selective isolation is not mandatory,” said Prof. Pohl-Albertyn.

The study also found C. auris in both the fore- and hindguts of the locusts. The foregut, responsible for food intake and partial digestion, likely serves as the entry point for the yeast via the locust’s feeding activities. The hindgut confirmed that C. auris can survive digestion and may be excreted back into the environment through faeces.
While C. auris poses a significant risk to individuals with compromised immune systems, Prof. Pohl-Albertyn emphasized that healthy humans are not at great risk. “There is currently no proof that ingestion may be harmful to them,” she explained. However, she warned that the yeast could pose dangers to immunocompromised individuals, even though few people in South Africa are in direct contact with locusts.
One of the C. auris strains studied in-depth showed decreased susceptibility to fluconazole, a common antifungal drug, underscoring the need for new antifungal treatments. “This highlights the urgent need to discover and develop new antifungal drugs,” Prof. Pohl-Albertyn added.
The study also raises concerns about how locusts could potentially spread C. auris to other animals, such as birds, and, in some regions, even humans. “The fact that locusts are a food source for other animals could lead to eventual distribution of the yeast to people,” Prof. Pohl-Albertyn noted. In countries where locusts are consumed by humans, direct transmission could be more likely.
This research contributes to understanding the natural hosts of emerging pathogens and their role in spreading these diseases. Prof. Pohl-Albertyn emphasized the importance of understanding how C. auris emerged as a pathogen in multiple countries and how environmental factors may have shaped its evolution. “This has implications for the prevention of the spread of this specific yeast species, as well as our preparedness for new pathogenic yeasts that may be emerging from the environment,” she concluded.
Earth
Life may have learned to breathe oxygen hundreds of millions of years earlier than thought

Early life on Earth has found an interetsing turning point. A new study by researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology suggests that some of Earth’s earliest life forms may have evolved the ability to use oxygen hundreds of millions of years before it became a permanent part of the planet’s atmosphere.
Oxygen is essential to most life on Earth today, but it was not always abundant. Scientists have long believed that oxygen only became a stable component of the atmosphere around 2.3 billion years ago, during a turning point known as the Great Oxidation Event (GOE). The new findings indicate that biological use of oxygen may have begun much earlier, potentially reshaping scientists’ understanding of how life evolved on Earth.
The study, published in the journal Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, traces the evolutionary origins of a key enzyme that allows organisms to use oxygen for aerobic respiration. This enzyme is present in most oxygen-breathing life forms today, from bacteria to humans.
Scientists have long believed that oxygen only became a stable component of the atmosphere around 2.3 billion years ago, during a turning point known as the Great Oxidation Event (GOE). The new findings indicate that biological use of oxygen may have begun much earlier, potentially reshaping scientists’ understanding of how life evolved on Earth
MIT geobiologists found that the enzyme likely evolved during the Mesoarchean era, between 3.2 and 2.8 billion years ago—several hundred million years before the Great Oxidation Event.
The findings may help answer a long-standing mystery in Earth’s history: why it took so long for oxygen to accumulate in the atmosphere. Scientists know that cyanobacteria, the first organisms capable of producing oxygen through photosynthesis, emerged around 2.9 billion years ago. Yet atmospheric oxygen levels remained low for hundreds of millions of years after their appearance.
While geochemical reactions with rocks were previously thought to be the main reason oxygen failed to build up early on, the MIT study suggests biology itself may also have played a role. Early organisms that evolved the oxygen-using enzyme may have consumed small amounts of oxygen as soon as it was produced, limiting how much could accumulate in the atmosphere.
“This does dramatically change the story of aerobic respiration,” said Fatima Husain, postdoctoral researcher in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, said in a media statement. “Our study adds to this very recently emerging story that life may have used oxygen much earlier than previously thought. It shows us how incredibly innovative life is at all periods in Earth’s history.”
The research team analysed thousands of genetic sequences of heme-copper oxygen reductases—enzymes essential for aerobic respiration—across a wide range of modern organisms. By mapping these sequences onto an evolutionary tree and anchoring them with fossil and geological evidence, the researchers were able to estimate when the enzyme first emerged.
“The puzzle pieces are fitting together and really underscore how life was able to diversify and live in this new, oxygenated world
Tracing the enzyme back through time, the team concluded that oxygen use likely appeared soon after cyanobacteria began producing oxygen. Organisms living close to these microbes may have rapidly consumed the oxygen they released, delaying its escape into the atmosphere.
“Considered all together, MIT research has filled in the gaps in our knowledge of how Earth’s oxygenation proceeded,” Husain said. “The puzzle pieces are fitting together and really underscore how life was able to diversify and live in this new, oxygenated world.”
The study adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that life on Earth adapted to oxygen far earlier than previously believed, offering new insights into how biological innovation shaped the planet’s atmosphere and the evolution of complex life.
The Sciences
Researchers crack greener way to mine lithium, cobalt and nickel from dead batteries
A breakthrough recycling method developed at Monash University in Australia can recover over 95% of critical metals from spent lithium-ion batteries—without extreme heat or toxic chemicals—offering a major boost to clean energy and circular economy goals.
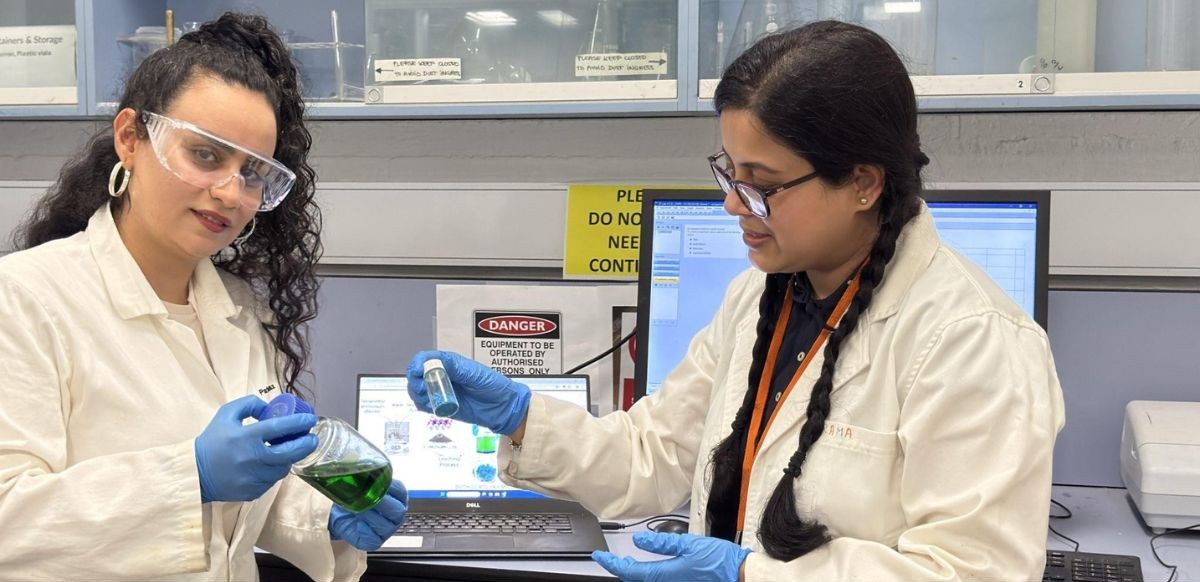

Researchers at Monash University, based in Melbourne, Australia, have developed a breakthrough, environmentally friendly method to recover high-purity nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries, offering a safer alternative to conventional recycling processes.
The new approach uses a mild and sustainable solvent, avoiding the high temperatures and hazardous chemicals typically associated with battery recycling. The innovation comes at a critical time, as an estimated 500,000 tonnes of spent lithium-ion batteries have already accumulated globally. Despite their growing volume, recycling rates remain low, with only around 10 per cent of spent batteries fully recycled in countries such as Australia.
Most discarded batteries end up in landfills, where toxic substances can seep into soil and groundwater, gradually entering the food chain and posing long-term health and environmental risks. This is particularly concerning given that spent lithium-ion batteries are rich secondary resources, containing strategic metals including lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, copper, aluminium and graphite.
Existing recovery methods often extract only a limited range of elements and rely on energy-intensive or chemically aggressive processes. The Monash team’s solution addresses these limitations by combining a novel deep eutectic solvent (DES) with an integrated chemical and electrochemical leaching process.
Dr Parama Banerjee, principal supervisor and project lead from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, said the new method achieves more than 95 per cent recovery of nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium, even from industrial-grade “black mass” that contains mixed battery chemistries and common impurities.

“This is the first report of selective recovery of high-purity Ni, Co, Mn, and Li from spent battery waste using a mild solvent,” Dr Banerjee said.
“Our process not only provides a safer, greener alternative for recycling lithium-ion batteries but also opens pathways to recover valuable metals from other electronic wastes and mine tailings.”
Parisa Biniaz, PhD student and co-author of the study, said the breakthrough represents a significant step towards a circular economy for critical metals while reducing the environmental footprint of battery disposal.
“Our integrated process allows high selectivity and recovery even from complex, mixed battery black mass. The research demonstrates a promising approach for industrial-scale recycling, recovering critical metals efficiently while minimising environmental harm,” Biniaz said.
The researchers say the method could play a key role in supporting sustainable energy transitions by securing critical mineral supplies while cutting down on environmental damage from waste batteries.
Sustainable Energy
Can ammonia power a low-carbon future? New MIT study maps global costs and emissions
Under what conditions can ammonia truly become a low-carbon energy solution? MIT researchers attempt to resolve this

Ammonia, long known as the backbone of global fertiliser production, is increasingly being examined as a potential pillar of the clean energy transition. Energy-dense, carbon-free at the point of use, and already traded globally at scale, ammonia is emerging as a candidate fuel and a carrier of hydrogen. But its climate promise comes with a contradiction: today’s dominant method of producing ammonia carries a heavy carbon footprint.
A new study by researchers from the MIT Energy Initiative (MITEI) attempts to resolve this tension by answering a foundational question for policymakers and industry alike: under what conditions can ammonia truly become a low-carbon energy solution?
A global view of ammonia’s future
In a paper published in Energy and Environmental Science, the researchers present the largest harmonised dataset to date on the economic and environmental impacts of global ammonia supply chains. The analysis spans 63 countries and evaluates multiple production pathways, trade routes, and energy inputs, offering a comprehensive view of how ammonia could be produced, shipped, and used in a decarbonising world.
“This is the most comprehensive work on the global ammonia landscape,” says senior author Guiyan Zang, a research scientist at MITEI. “We developed many of these frameworks at MIT to be able to make better cost-benefit analyses. Hydrogen and ammonia are the only two types of fuel with no carbon at scale. If we want to use fuel to generate power and heat, but not release carbon, hydrogen and ammonia are the only options, and ammonia is easier to transport and lower-cost.”
Why data matters
Until now, assessments of ammonia’s climate potential have been fragmented. Individual studies often focused on single regions, isolated technologies, or only cost or emissions, making global comparisons difficult.
“Before this, there were no harmonized datasets quantifying the impacts of this transition,” says lead author Woojae Shin, a postdoctoral researcher at MITEI. “Everyone is talking about ammonia as a super important hydrogen carrier in the future, and also ammonia can be directly used in power generation or fertilizer and other industrial uses. But we needed this dataset. It’s filling a major knowledge gap.”
To build the database, the team synthesised results from dozens of prior studies and applied common frameworks to calculate full lifecycle emissions and costs. These calculations included feedstock extraction, production, storage, shipping, and import processing, alongside country-specific factors such as electricity prices, natural gas costs, financing conditions, and energy mix.
Comparing production pathways
Today, most ammonia is produced using the Haber–Bosch process powered by fossil fuels, commonly referred to as “grey ammonia.” In 2020, this process accounted for about 1.8 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. While economically attractive, it is also the most carbon-intensive option.
The study finds that conventional grey ammonia produced via steam methane reforming (SMR) remains the cheapest option in the U.S. context, at around 48 cents per kilogram. However, it also carries the highest emissions, at 2.46 kilograms of CO₂ equivalent per kilogram of ammonia.
Cleaner alternatives offer substantial emissions reductions at higher cost. Pairing SMR with carbon capture and storage cuts emissions by about 61 percent, with a 29 percent cost increase. A full global shift to ammonia produced with conventional methods plus carbon capture could reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by nearly 71 percent, while raising costs by 23.2 percent.
More advanced “blue ammonia” pathways, such as auto-thermal reforming (ATR) with carbon capture, deliver deeper emissions cuts at relatively modest cost increases. One ATR configuration achieved emissions of 0.75 kilograms of CO₂ equivalent per kilogram of ammonia, at roughly 10 percent higher cost than conventional SMR.
At the far end of the spectrum, “green ammonia” produced using renewable electricity can reduce emissions by as much as 99.7 percent, but at a significantly higher cost—around 46 percent more than today’s baseline. Ammonia produced using nuclear electricity showed near-zero emissions in the analysis.
Geography matters
The study also reveals that the viability of low-carbon ammonia depends heavily on geography. Countries with abundant, low-cost natural gas are better positioned to produce blue ammonia competitively, while regions with cheap renewable electricity are more favourable for green ammonia.
China emerged as a potential future supplier of green ammonia to multiple regions, while parts of the Middle East showed strong competitiveness in low-carbon ammonia production. In contrast, ammonia produced using carbon-intensive grid electricity was often both more expensive and more polluting than conventional methods.
From research to policy
Interest in low-carbon ammonia is no longer theoretical. Countries such as Japan and South Korea have incorporated ammonia into national energy strategies, including pilot projects using ammonia for power generation and financial incentives tied to verified emissions reductions.
“Ammonia researchers, producers, as well as government officials require this data to understand the impact of different technologies and global supply corridors,” Shin says.
Zang adds that the dataset is designed not just as an academic exercise, but as a decision-making tool. “We collaborate with companies, and they need to know the full costs and lifecycle emissions associated with different options. Governments can also use this to compare options and set future policies. Any country producing ammonia needs to know which countries they can deliver to economically.”
As global demand for low-carbon fuels accelerates toward mid-century, the study suggests that ammonia’s role will depend less on ambition alone, and more on informed choices—grounded in data—about how and where it is produced.
-

 Society2 months ago
Society2 months agoThe Ten-Rupee Doctor Who Sparked a Health Revolution in Kerala’s Tribal Highlands
-

 COP304 months ago
COP304 months agoBrazil Cuts Emissions by 17% in 2024—Biggest Drop in 16 Years, Yet Paris Target Out of Reach
-

 Earth4 months ago
Earth4 months agoData Becomes the New Oil: IEA Says AI Boom Driving Global Power Demand
-

 Society2 months ago
Society2 months agoFrom Qubits to Folk Puppetry: India’s Biggest Quantum Science Communication Conclave Wraps Up in Ahmedabad
-

 COP304 months ago
COP304 months agoCorporate Capture: Fossil Fuel Lobbyists at COP30 Hit Record High, Outnumbering Delegates from Climate-Vulnerable Nations
-

 Space & Physics3 months ago
Space & Physics3 months agoIndian Physicists Win 2025 ICTP Prize for Breakthroughs in Quantum Many-Body Physics
-

 Women In Science5 months ago
Women In Science5 months agoThe Data Don’t Lie: Women Are Still Missing from Science — But Why?
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoAir Pollution Claimed 1.7 Million Indian Lives and 9.5% of GDP, Finds The Lancet