Space & Physics
Exotic black holes might be a result of dark matter
MIT physicists propose that in the first quintillionth of a second, the universe may have produced microscopic black holes with immense nuclear charge.

Fifty years ago, physicist Stephen Hawking proposed a theory about dark matter, suggesting it might consist of a population of black holes formed shortly after the Big Bang. These “primordial” black holes would be vastly different from the massive ones we observe today. Instead, they would be tiny regions of ultradense matter, created within the first quintillionth of a second following the Big Bang. These microscopic black holes would then collapse and disperse throughout the universe, influencing space-time in ways that could account for the dark matter we recognize today.
Now, MIT physicists discovered that this primordial process would have also generated some surprising companions: even smaller black holes with unprecedented levels of a nuclear-physics property called “color charge.”
These smallest, “super-charged” black holes would represent an entirely new state of matter, likely evaporating within a fraction of a second after forming. Despite their brief existence, they could have influenced a crucial cosmological transition: the formation of the first atomic nuclei. The physicists propose that these color-charged black holes might have affected the balance of fusing nuclei, a phenomenon that astronomers might detect with future measurements. Such observations would strongly suggest that primordial black holes are the source of all dark matter today.
“Even though these short-lived, exotic creatures are not around today, they could have affected cosmic history in ways that could show up in subtle signals today,” says David Kaiser, the Germeshausen Professor of the History of Science and professor of physics at MIT. “Within the idea that all dark matter could be accounted for by black holes, this gives us new things to look for.”
Kaiser and his co-author, MIT graduate student Elba Alonso-Monsalve, have published their study in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Space & Physics
Researchers Develop Stretchable Material That Can Instantly Switch How It Conducts Heat
MIT engineers have developed a stretchable material heat conduction system that can rapidly switch how heat flows, enabling adaptive cooling applications.
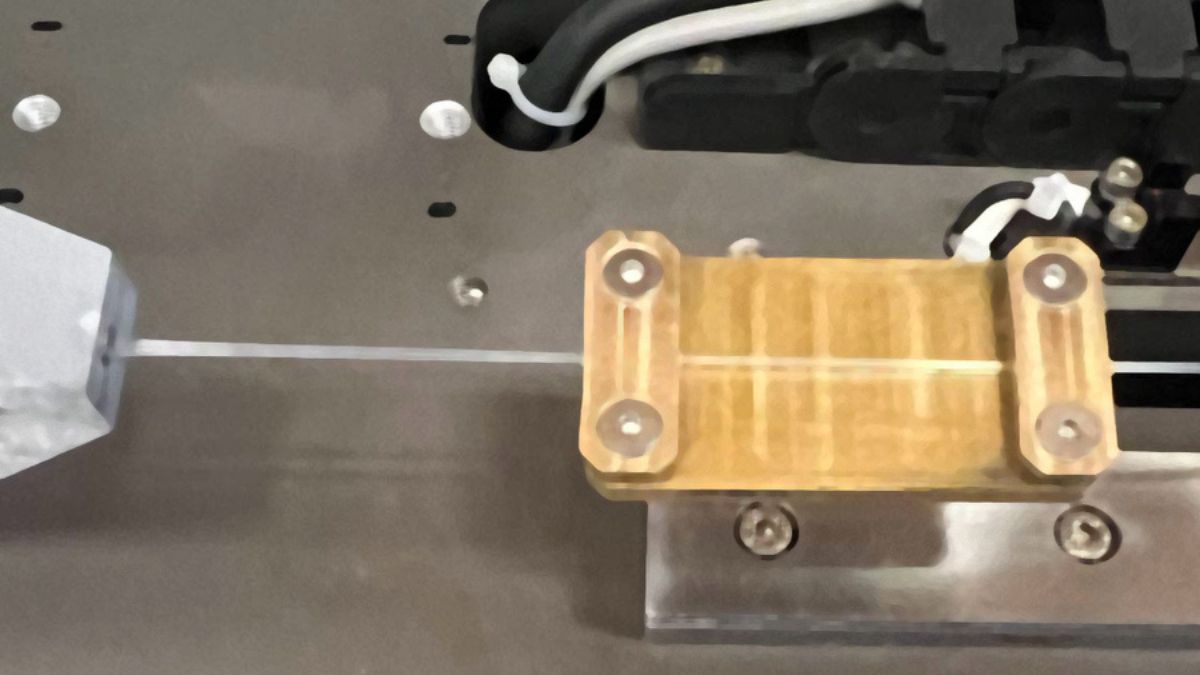
Stretchable material heat conduction has taken a major leap forward as engineers at MIT have developed a polymer that can rapidly and reversibly switch how it conducts heat simply by being stretched. The discovery opens new possibilities for adaptive cooling technologies in clothing, electronics, and building infrastructure.
Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have developed a new polymer material that can rapidly and reversibly switch how it conducts heat—simply by being stretched.
The research shows that a commonly used soft polymer, known as an olefin block copolymer (OBC), can more than double its thermal conductivity when stretched, shifting from heat-handling behaviour similar to plastic to levels closer to marble. When the material relaxes back to its original form, its heat-conducting ability drops again, returning to its plastic-like state.
The transition happens extremely fast—within just 0.22 seconds—making it the fastest thermal switching ever observed in a material, according to the researchers.
The findings open up possibilities for adaptive materials that respond to temperature changes in real time, with potential applications ranging from cooling fabrics and wearable technology to electronics, buildings, and infrastructure.
The research team initially began studying the material while searching for more sustainable alternatives to spandex, a petroleum-based elastic fabric that is difficult to recycle. During mechanical testing, the researchers noticed unexpected changes in how the polymer handled heat as it was stretched and released.
A new direction for adaptive materials
“We need materials that are inexpensive, widely available, and able to adapt quickly to changing environmental temperatures,” said Svetlana Boriskina, principal research scientist in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, in a media statement. She explained that the discovery of rapid thermal switching in this polymer creates new opportunities to design materials that actively manage heat rather than passively resisting it.
The research team initially began studying the material while searching for more sustainable alternatives to spandex, a petroleum-based elastic fabric that is difficult to recycle. During mechanical testing, the researchers noticed unexpected changes in how the polymer handled heat as it was stretched and released.
“What caught our attention was that the material’s thermal conductivity increased when stretched and decreased again when relaxed, even after thousands of cycles,” said Duo Xu, a co-author of the study, in a media statement. He added that the effect was fully reversible and occurred while the material remained largely amorphous, which contradicted existing assumptions in polymer science.
The discovery demonstrates how stretchable material heat conduction can be actively controlled in real time, allowing materials to respond dynamically to temperature changes.
How stretching unlocks heat flow
At the microscopic level, most polymers consist of tangled chains of carbon atoms that block heat flow. The MIT team found that stretching the olefin block copolymer temporarily straightens these tangled chains and aligns small crystalline regions, creating clearer pathways for heat to travel through the material.
“This gives the material the ability to toggle its heat conduction thousands of times without degrading
Unlike earlier work on polyethylene—where similar alignment permanently increased thermal conductivity—the new material does not crystallise under strain. Instead, its internal structure switches back and forth between straightened and tangled states, allowing repeated and reversible thermal switching.
“This gives the material the ability to toggle its heat conduction thousands of times without degrading,” Xu said.
From smart clothing to cooler electronics
The researchers say the material could be engineered into fibres for clothing that normally retain heat but instantly dissipate excess warmth when stretched. Similar concepts could be applied to electronics, laptops, and buildings, where materials could respond dynamically to overheating without external cooling systems.
“The difference in heat dissipation is similar to the tactile difference between touching plastic and touching marble,” Boriskina said in a media statement, highlighting how noticeable the effect can be.
The team is now working on optimising the polymer’s internal structure and exploring related materials that could produce even larger thermal shifts.
“If we can further enhance this effect, the industrial and societal impact could be substantial,” Boriskina said.
Researchers say advances in stretchable material heat conduction could significantly influence future designs of smart textiles, electronics cooling, and energy-efficient buildings.
The study has been published in the journal Advanced Materials. The authors include researchers from MIT and the Southern University of Science and Technology in China.
Researchers say advances in stretchable material heat conduction could significantly influence future designs of smart textiles, electronics cooling, and energy-efficient buildings.
Space & Physics
Physicists Capture ‘Wakes’ Left by Quarks in the Universe’s First Liquid
Scientists at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider have observed, for the first time, fluid-like wakes created by quarks moving through quark–gluon plasma, offering direct evidence that the universe’s earliest matter behaved like a liquid rather than a cloud of free particles.
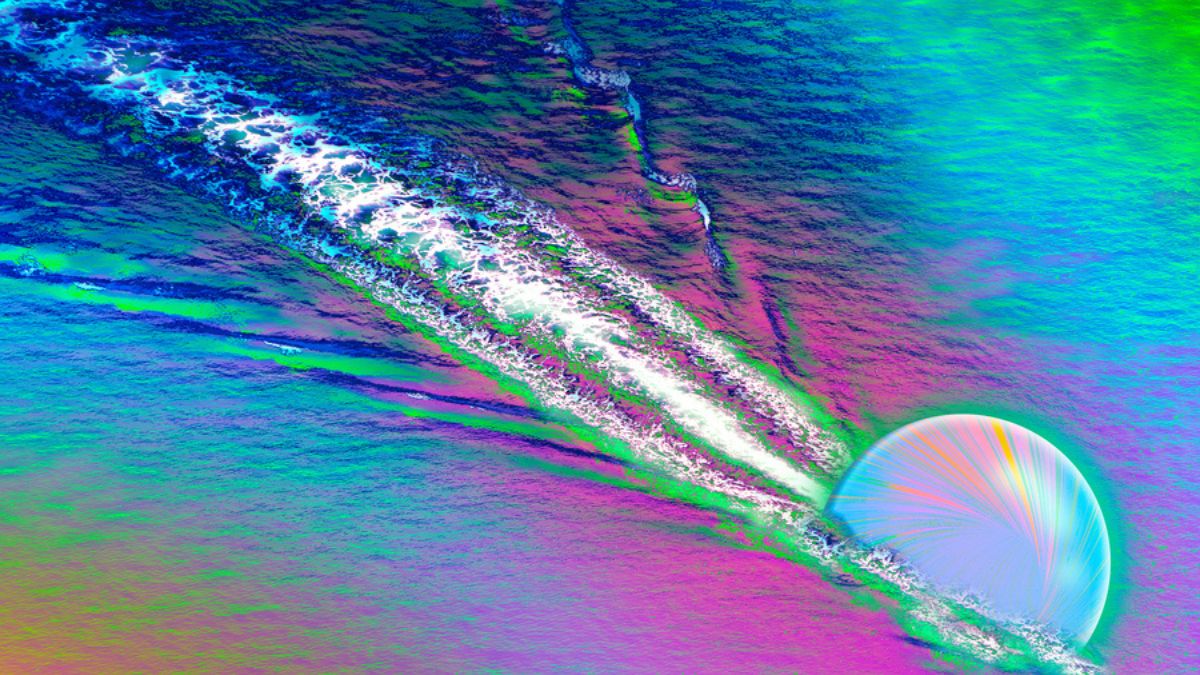
Physicists working at the CERN(The European Organization for Nuclear Research) have reported the first direct experimental evidence that quark–gluon plasma—the primordial matter that filled the universe moments after the Big Bang—behaves like a true liquid.
Using heavy-ion collisions at the Large Hadron Collider, researchers recreated the extreme conditions of the early universe and observed that quarks moving through this plasma generate wake-like patterns, similar to ripples trailing a duck across water.
The study, led by physicists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, shows that the quark–gluon plasma responds collectively, flowing and splashing rather than scattering randomly.
“It has been a long debate in our field, on whether the plasma should respond to a quark,” said Yen-Jie Lee in a media statement. “Now we see the plasma is incredibly dense, such that it is able to slow down a quark, and produces splashes and swirls like a liquid. So quark-gluon plasma really is a primordial soup.”
Quark–gluon plasma is believed to be the first liquid to have existed in the universe and the hottest ever observed, reaching temperatures of several trillion degrees Celsius. It is also considered a near-perfect liquid, flowing with almost no resistance.
To isolate the wake produced by a single quark, the team developed a new experimental technique. Instead of tracking pairs of quarks and antiquarks—whose effects can overlap—they identified rare collision events that produced a single quark traveling in the opposite direction of a Z boson. Because a Z boson interacts weakly with its surroundings, it acts as a clean marker, allowing scientists to attribute any observed plasma ripples solely to the quark.
“We have figured out a new technique that allows us to see the effects of a single quark in the QGP, through a different pair of particles,” Lee said.
Analysing data from around 13 billion heavy-ion collisions, the researchers identified roughly 2,000 Z-boson events. In these cases, they consistently observed fluid-like swirls in the plasma opposite to the Z boson’s direction—clear signatures of quark-induced wakes.
The results align with theoretical predictions made by MIT physicist Krishna Rajagopal, whose hybrid model suggested that quarks should drag plasma along as they move through it.
“This is something that many of us have argued must be there for a good many years, and that many experiments have looked for,” Rajagopal said.
“We’ve gained the first direct evidence that the quark indeed drags more plasma with it as it travels,” Lee added. “This will enable us to study the properties and behavior of this exotic fluid in unprecedented detail.”
The research was carried out by members of the CMS Collaboration using the Compact Muon Solenoid detector at CERN. The open-access study has been published in the journal Physics Letters B.
Space & Physics
Why Jupiter Has Eight Polar Storms — and Saturn Only One: MIT Study Offers New Clues
Two giant planets, made of the same elements, display radically different storms at their poles. New research from MIT now suggests that the key to this cosmic mystery lies not in the skies, but deep inside Jupiter and Saturn themselves.
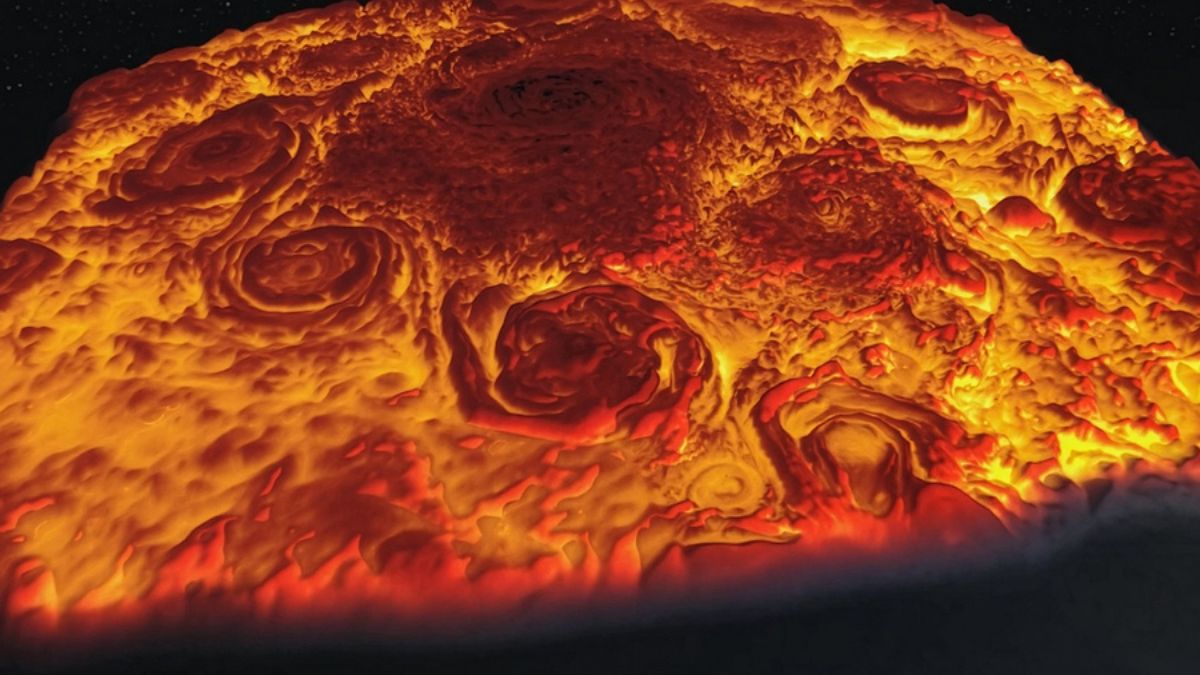
For decades, spacecraft images of Jupiter and Saturn have puzzled planetary scientists. Despite being similar in size and composition, the two gas giants display dramatically different weather systems at their poles. Jupiter hosts a striking formation: a central polar vortex encircled by eight massive storms, resembling a rotating crown. Saturn, by contrast, is capped by a single enormous cyclone, shaped like a near-perfect hexagon.
Now, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology believe they have identified a key reason behind this cosmic contrast — and the answer may lie deep beneath the planets’ cloud tops.
In a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the MIT team suggests that the structure of a planet’s interior — specifically, how “soft” or “hard” the base of a vortex is — determines whether polar storms merge into one giant system or remain as multiple smaller vortices.
“Our study shows that, depending on the interior properties and the softness of the bottom of the vortex, this will influence the kind of fluid pattern you observe at the surface,” says study author Wanying Kang, assistant professor in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS) in a media release issued by the institute. “I don’t think anyone’s made this connection between the surface fluid pattern and the interior properties of these planets. One possible scenario could be that Saturn has a harder bottom than Jupiter.”
A long-standing planetary mystery
The contrast has been visible for years thanks to two landmark NASA missions. The Juno spacecraft, which has been orbiting Jupiter since 2016, revealed a dramatic polar arrangement of swirling storms, each roughly 3,000 miles wide — nearly half the diameter of Earth. Cassini, which orbited Saturn for 13 years before its mission ended in 2017, documented the planet’s iconic hexagonal polar vortex, stretching nearly 18,000 miles across.
“People have spent a lot of time deciphering the differences between Jupiter and Saturn,” says Jiaru Shi, the study’s first author and an MIT graduate student. “The planets are about the same size and are both made mostly of hydrogen and helium. It’s unclear why their polar vortices are so different.”
Simulating storms on gas giants
To tackle the question, the researchers turned to computer simulations. They created a two-dimensional model of atmospheric flow designed to mimic how storms might evolve on a rapidly rotating gas giant.
While real planetary vortices are three-dimensional, the team argued that Jupiter’s and Saturn’s fast spin simplifies the physics. “In a fast-rotating system, fluid motion tends to be uniform along the rotating axis,” Kang explains. “So, we were motivated by this idea that we can reduce a 3D dynamical problem to a 2D problem because the fluid pattern does not change in 3D. This makes the problem hundreds of times faster and cheaper to simulate and study.”
The model allowed the scientists to test thousands of possible planetary conditions, varying factors such as rotation rate, internal heating, planet size and — crucially — the density of material beneath the vortices. Each simulation began with random chaotic motion and tracked how storms evolved over time.
The outcomes consistently fell into two categories: either the system developed one dominant polar vortex, like Saturn, or several coexisting vortices, like Jupiter.
The decisive factor turned out to be how much a vortex could grow before being constrained by the properties of the layers beneath it.
When the lower layers were made of softer, lighter material, individual vortices could not expand indefinitely. Instead, they stabilized at smaller sizes, allowing multiple storms to coexist at the pole. This matches what scientists observe on Jupiter.
But when the simulated vortex base was denser and more rigid, vortices were able to grow larger and eventually merge. The end result was a single, planet-scale storm — remarkably similar to Saturn’s massive polar cyclone.
“This equation has been used in many contexts, including to model midlatitude cyclones on Earth,” Kang says. “We adapted the equation to the polar regions of Jupiter and Saturn.”
The findings suggest that Saturn’s interior may contain heavier elements or more condensed material than Jupiter’s, giving its atmospheric vortices a firmer foundation to build upon.
“What we see from the surface, the fluid pattern on Jupiter and Saturn, may tell us something about the interior, like how soft the bottom is,” Shi says. “And that is important because maybe beneath Saturn’s surface, the interior is more metal-enriched and has more condensable material which allows it to provide stronger stratification than Jupiter. This would add to our understanding of these gas giants.”
Reading the interiors from the skies
Planetary scientists have long struggled to infer the internal structures of gas giants, where pressures and temperatures are far beyond what can be reproduced in laboratories. This new work offers a rare bridge between visible atmospheric patterns and hidden planetary composition.
Beyond explaining two of the Solar System’s most visually striking storms, the research could shape how scientists interpret observations of distant exoplanets as well — worlds where atmospheric patterns might be the only clues to what lies within.
For now, Jupiter’s swirling crown of storms and Saturn’s solitary hexagon may be doing more than decorating the poles of two distant giants. They may be quietly revealing the deep, unseen architecture of the planets themselves.
-

 Society2 months ago
Society2 months agoThe Ten-Rupee Doctor Who Sparked a Health Revolution in Kerala’s Tribal Highlands
-

 COP304 months ago
COP304 months agoBrazil Cuts Emissions by 17% in 2024—Biggest Drop in 16 Years, Yet Paris Target Out of Reach
-

 Earth4 months ago
Earth4 months agoData Becomes the New Oil: IEA Says AI Boom Driving Global Power Demand
-

 Society2 months ago
Society2 months agoFrom Qubits to Folk Puppetry: India’s Biggest Quantum Science Communication Conclave Wraps Up in Ahmedabad
-

 COP304 months ago
COP304 months agoCorporate Capture: Fossil Fuel Lobbyists at COP30 Hit Record High, Outnumbering Delegates from Climate-Vulnerable Nations
-

 Space & Physics3 months ago
Space & Physics3 months agoIndian Physicists Win 2025 ICTP Prize for Breakthroughs in Quantum Many-Body Physics
-

 Women In Science5 months ago
Women In Science5 months agoThe Data Don’t Lie: Women Are Still Missing from Science — But Why?
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoAir Pollution Claimed 1.7 Million Indian Lives and 9.5% of GDP, Finds The Lancet






































