Earth
$4.3 Trillion Economic Loss: The Rising Cost of Climate Change and the Urgent Need for Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems, which are proven to reduce the economic and human costs of extreme weather, remain inaccessible to nearly half of the world’s countries
The world is paying an increasingly heavy price for the devastating effects of climate change. In the last five decades alone, global economic losses due to weather, climate, and water-related disasters have soared to an eye-watering $4.3 trillion. The death toll, though falling, remains tragically high with over 2 million people having lost their lives to these extreme events. As the planet continues to heat up, with 2024 marked as the hottest year on record, the financial toll of these disasters is only set to rise.
The problem isn’t just the scale of these losses, but the lack of adequate systems in place to mitigate them. Early warning systems, which are proven to reduce the economic and human costs of extreme weather, remain inaccessible to nearly half of the world’s countries. While the technology exists, the disparity in access to life-saving forecasting and warning systems is leaving millions vulnerable to storms, floods, wildfires, and droughts that could otherwise be anticipated.

“We are more than just weather forecasters,” said Celeste Saulo, Secretary-General of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), which recently marked its 75th anniversary. “WMO makes the world safer, more secure, and prosperous.” Yet, despite decades of advancements in forecasting, gaps remain. Countries with limited resources struggle to set up the infrastructure needed to protect their populations, which often face the brunt of the most severe consequences of climate change.
In his message for World Meteorological Day, UN Secretary-General António Guterres highlighted the stark reality: “It is disgraceful that, in a digital age, lives and livelihoods are being lost because people have no access to effective early warning systems.” The warning from Guterres couldn’t be clearer: early warning systems are not luxuries. They are necessities—and crucial investments that offer nearly a ten-fold return.
The data is irrefutable. From satellite feeds to ocean buoys, billions of measurements are collected daily from across the globe. Yet, in many parts of the world, these critical insights into climate and weather patterns do not reach those who need them most. Gaps in observation networks and forecasting accuracy continue to undermine the ability of vulnerable communities to prepare for and respond to disasters.
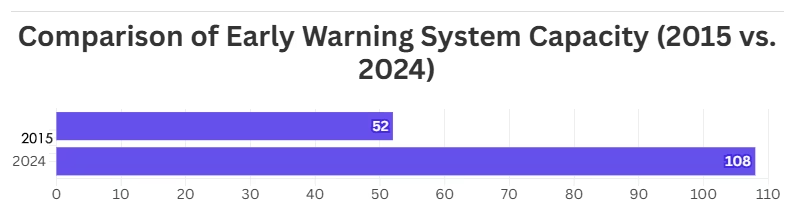
WMO’s Early Warnings for All initiative seeks to address this crisis by ensuring that by 2027, every country, no matter how economically or technologically challenged, has access to effective early warning systems. As of 2024, 108 countries report some capacity for multi-hazard early warning systems—more than double the number from 2015. However, this progress is not fast enough to prevent future calamities. The economic costs of inaction are simply too high.
| Key Data Points |
|---|
| $4.3 Trillion – Total global economic losses from weather, climate, and water-related hazards between 1970 and 2021. |
| 2 Million+ – Number of lives lost to weather, climate, and water-related disasters between 1970 and 2021. |
| 108 Countries – The number of countries with some capacity for multi-hazard early warning systems as of 2024, more than double the 52 countries in 2015. |
| $1 Investment in Early Warning Systems – The potential return on investment is nearly ten times the cost, according to UN Secretary-General António Guterres. |
| 2024 – The year marked as the hottest year on record. |
| 75 Years – The number of years the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has been a UN specialized agency, working to improve global resilience to climate change. |
| Source: WMO |
Between 1970 and 2021, climate-related disasters cost the global economy $4.3 trillion—a figure that continues to climb year after year. Without early warnings, this loss is compounded by the inability of countries to adapt or respond in time, resulting in more widespread destruction and human suffering. But for every dollar invested in early warning systems, the potential savings and lives saved are immense.
“The staff of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services are like doctors and nurses – working 24/7 to safeguard and promote public well-being,” Saulo emphasized. These services are crucial for monitoring climate and weather changes and issuing warnings, but much of the world’s population still lacks access to these vital resources.
WMO’s call to action on World Meteorological Day, though after the fact, remains urgent: “We need high-level political support, increased technology sharing, greater collaboration between governments and businesses, and a major effort to scale-up finance,” said Guterres. He emphasized the importance of boosting the lending capacity of multilateral development banks to ensure that resources reach the nations most at risk.
As the planet faces increasingly volatile climate conditions, the economic costs of inaction are mounting. Without the necessary investment in early warning systems, millions will continue to suffer, and the global economy will pay the price. The time to act is now. Climate change may be an overwhelming challenge, but with the right systems in place, we can mitigate the damage, save lives, and protect our collective future.
Earth
Global Report Reveals Planetary Health Communication Crisis Fuelled by AI and Misinformation
Global report reveals planetary health communication crisis fuelled by AI misinformation threatens climate action and vulnerable communities.

A new report launched yesterday at the Planetary Health Annual Meeting in Rotterdam has exposed a critical failure in global health communication that experts warn could undermine humanity’s response to interconnected climate and health crises.
The comprehensive study, titled “Voices for Planetary Health: Leveraging AI, Media and Stakeholder Strengths for Effective Narratives to Advance Planetary Health,” represents the first systematic mapping of how planetary health issues are communicated worldwide. Developed by the Sunway Centre for Planetary Health at Sunway University and implemented by Internews, the research reveals that communication—not scientific knowledge—has become the critical bottleneck preventing effective action on environmental health emergencies.
Fragmented Messages
The study’s findings paint a troubling picture of the global communication landscape. Despite mounting scientific evidence about the interconnected health threats from climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution, public discourse remains severely fragmented and increasingly vulnerable to misinformation.
“We know the science. What we lack is a shared story that resonates across communities, cultures, and decision-makers,” said Prof. Dr. Jemilah Mahmood, Executive Director of the Sunway Centre for Planetary Health.

The research, which analyzed 96 organizations and individuals across nine countries through in-depth interviews and social media analysis, found that planetary health communication efforts are often siloed within specific disciplines, limiting their reach and effectiveness. Many initiatives depend on short-term projects with minimal resources, leaving little capacity to build sustained narratives that could drive meaningful policy change.
AI: Double-Edged Sword
Perhaps most concerning is the report’s revelation about artificial intelligence’s dual role in planetary health communication. While AI presents opportunities for expanding access to reliable information and supporting multilingual communication, it also poses significant risks for spreading misinformation and deepening inequality.
Recent studies have documented how generative AI can be weaponized to create climate misinformation through bot-generated tweets mimicking climate deniers, deep-fake images of environmental activists, and sophisticated long-form content espousing false narratives. The technology can also amplify existing biases, with research showing that AI systems often privilege Western knowledge over Indigenous perspectives, potentially contributing to “global conservation injustices”.
The environmental cost of AI itself compounds the problem. Data centres now consume around 1.5% of global electricity, with AI-focused facilities requiring as much power as energy-intensive aluminium smelters. Training large language models like GPT-4 requires three to five times more energy than GPT-3, which already consumes enough electricity to power 120 American homes for a year.
Marginalized Communities Bear the Heaviest Burden
The communication crisis disproportionately impacts the world’s most vulnerable populations—precisely those most affected by planetary health emergencies. The report emphasizes that marginalized communities, including people of colour, low-income groups, and Indigenous peoples, face the greatest challenges in both accessing reliable health information and adapting to climate-related health threats.
Multiple studies confirm that racially and socioeconomically marginalized communities in the United States experience greater impacts from climate-related health events, including extreme heat, flooding, and respiratory illnesses. Children of colour are particularly vulnerable, experiencing disproportionate health impacts from climate exposures compared to white children.
The communication barriers compound these vulnerabilities. Scientific jargon makes planetary health concepts inaccessible to general audiences, while language delivery challenges—including complex English or lack of translation—further limit reach to non-English speaking communities.
Despite the communication challenges, the report identifies young people as both critical audiences and powerful communicators, particularly through digital platforms. Youth activists are increasingly using social media to drive environmental awareness and policy pressure, though they face significant obstacles including algorithmic bias and platform censorship concerns.
The research found that LinkedIn was most effective for professional audiences, while Instagram and TikTok showed promise for youth engagement, despite trust issues on some platforms. However, maintaining consistent and meaningful social media presence remains challenging for many organizations working with limited resources.
Strategic Solutions
To address these critical communication failures, the report proposes a revolutionary two-pronged strategy combining “strategic communication” to influence policy with “democratic communication” to foster community-level dialogue.
The approach rests on six core principles: ensuring marginalized voices shape the agenda; presenting planetary health as an integrated framework rather than disconnected crises; building bridges between disciplines and geographies; anticipating backlash and protecting communicators; tailoring messages to cultural contexts; and working within existing cognitive frameworks.
The research team has developed practical playbooks for different stakeholder groups and monitoring frameworks to track communication effectiveness—tools they argue could be transformative if adopted widely across the planetary health community.
“Communication is not just a tool; it is a catalyst for change. By speaking with courage, coherence, and compassion, and equipping all actors to tell inclusive stories, we can turn knowledge into action and ensure no voice is left behind,” said Jayalakshmi Shreedhar of Internews.

The report’s launch comes at a critical moment, as policy rollbacks in major economies threaten to undermine decades of environmental progress. The study documents how recent reversals, including the United States’ withdrawal from climate agreements and defunding of health agencies, have weakened the systemic response needed to address planetary health crises.
With six of nine planetary boundaries already crossed and climate-related health impacts accelerating globally, experts warn that the window for effective communication and coordinated action is rapidly closing. The success of humanity’s response to interconnected environmental and health crises may ultimately depend on our ability to tell a coherent, compelling story that mobilizes action across all levels of society.
Earth
Bridging the Adaptation Finance Gap: India’s Case Before COP30
As COP30 approaches, India faces a widening adaptation finance gap, despite rising climate impacts and mounting economic losses

With COP30 in Brazil less than a month away, the world’s attention is turning to the elusive promise of adaptation finance — money meant not for cutting emissions, but for surviving their consequences. In New Delhi this week, a closed-door High-Level Roundtable on Adaptation Finance, organised by Climate Trends, brought together senior policymakers, economists, and global climate finance experts. The message that emerged was stark: India’s adaptation needs are vast, but the money isn’t flowing.
According to international estimates, while adaptation finance globally rose from USD 22 billion to USD 28 billion in 2022, developing countries require more than USD 350 billion annually to protect lives and livelihoods. India’s share of that unmet need remains enormous — and more than 60% of global adaptation finance still comes as loans, piling additional debt on already stressed economies.
“The geopolitics of the world is at an inflection point,” said Aarti Khosla, Director of Climate Trends. “Countries are wrestling with how to make the Global Goal on Adaptation practical and measurable. India is preparing to submit its first National Adaptation Plan. The quality of the finance also matters — because commitments made at multilateral fora are only as good as the systems that deliver them.”
The Growing Cost of Climate Impacts
India’s climate vulnerabilities are intensifying. Record-breaking heatwaves, erratic monsoons, floods, and agricultural losses have already dented GDP growth, with studies suggesting climate-linked economic damage could shave off 2–3% of India’s GDP by 2030. The country’s adaptation costs, as projected by several national and international assessments, could run into tens of billions annually.
Yet, domestic and international systems remain mismatched to that reality. “Adaptation needs to be built into a profitable market system that attracts private investment and creates entrepreneurial enterprise,” argued Abhishek Acharya, Director at the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC). “We need a strong policy framework that enables even the last tier of governance — municipalities, panchayats — to access funding.”
The challenge, experts noted, isn’t just about the quantum of funds, but their design. India’s adaptation funding is fragmented across ministries and states, with little clarity on effectiveness. “We should be looking at adaptation-relevant expenditures,” said Amrita Goldar, Senior Fellow at the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER). “Looking through budgets at both central and state levels is a big task by itself. For adaptation, we don’t even have a sense of how technologies will evolve. When technologies are niche, private finance will not lead — public finance must.”
The Global Architecture and Local Realities
The Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA), first established under the Paris Agreement, remains largely conceptual — a vision still waiting for metrics. COP30 could change that, with countries expected to finalise indicators for tracking adaptation progress. Yet, experts warn that measurement alone won’t build resilience.
“If GGA indicators get finalised at COP30, they will become a yardstick for evaluation and performance,” said Pushp Bajaj, Programme Lead at Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW). “But just measuring progress isn’t enough. The connections with real climate challenges must be explicit, and India should take a strong stand.”
For India, where agriculture, water, health, and heat stress are already colliding crises, effective adaptation requires reforming both global finance flows and domestic fiscal systems. Kathryn Miliken, Senior Climate Change Specialist at the Asian Development Bank (ADB), noted that adaptation finance forms only about 10% of total climate finance worldwide. “ADB is aiming for 30% of its portfolio to go toward adaptation,” she said. “But the larger challenge is mainstreaming adaptation into economic planning. It still hangs loosely as a standalone agenda.”
Governance Gaps and Subnational Needs
At the state and district levels, limited financial autonomy has hindered locally relevant adaptation measures. Arjun Dutt of CEEW observed, “Coastal embankments, water shelters — these are public goods. Local authorities are directly involved, but though we have devolution in the Constitution, financial powers have not been devolved.”
Experts argued that subnational access to climate finance — through mechanisms like resilience bonds, blended finance, and state adaptation funds — could be the next big step. “Adaptation is a local issue,” said Amir Bazaz, Head of Infrastructure and Climate at the Indian Institute for Human Settlements (IIHS). “We don’t have the capacity to develop projects that are locally embedded, and resources are insufficient. Investments are largely driven by returns, not resilience.”
The Politics of Adaptation
Beyond numbers, adaptation is deeply political. “We understand the global game of power evolving around energy,” said Ambassador Manjeev S. Puri, Distinguished Fellow at TERI. “It’s time for us to talk about adaptation in a louder manner — both locally and globally. Link adaptation to resilience, and you will find political buy-in.”
Ovais Sarmad, Vice Chair of the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, added a sobering global view: “We’re living in a world that’s moved from VUCA — volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous — to BANI — brittle, anxious, non-linear, incomprehensible. India must be actively engaged in discussions at the Standing Committee on Finance. Our position must be clear and people-centred.”
The Standing Committee on Finance (SCF), part of the UNFCCC structure, plays a key role in shaping how climate funds are allocated and monitored — including reforms in Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs). Several participants at the roundtable called for MDBs to increase concessional finance and reduce the loan-heavy structure of current adaptation flows.
Data, Delivery, and Diplomacy
For experts like Purnamita Dasgupta, Head of the Environmental and Resource Economics Unit at the Institute for Economic Growth, the way forward lies in clarity and pragmatism. “We want a lot of things, but we need to split this conversation into high-level messages and those we keep within our borders,” she said. “There’s no case for being overwhelmed. Development is the only solution. We should not wait for a magic number, nor ignore it.”
The final consensus from the roundtable was clear: India’s leadership on adaptation finance will depend on how well it aligns data, policy, and diplomacy. As the country prepares to submit its first National Adaptation Plan (NAP) to the UNFCCC, its approach could influence not just negotiations at COP30, but also how the Global South reframes adaptation as a cornerstone of economic growth.
“Adaptation is no longer a technical footnote to mitigation,” Khosla concluded. “It’s about protecting people, ensuring justice, and redesigning the financial systems that decide who gets to survive the climate crisis — and how.”
Earth
Madhya Pradesh: Crop Damage Due to Excessive Rain—What Could Be the Solution?
Excessive rains in Madhya Pradesh have destroyed crops across villages like Chirai and Kesli, leaving farmers’ livelihoods at risk. Experts suggest simple solutions like drainage channels and raised-bed sowing to protect fields and build resilience against erratic monsoons.

This year, too, the monsoon in India brought not the usual promise of prosperity but widespread destruction, as it has in recent years. Torrential rains flooded farmlands across several states, washing away livelihoods and submerging the hopes of millions of farmers. Instead of irrigating the fields, the rain turned into an unrelenting deluge. States like Punjab, Maharashtra, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh experienced heavy flooding that claimed lives, displaced thousands, and devastated crops — a major blow to the country’s agricultural economy.
When rain becomes a curse
Madhya Pradesh, often called the “Heart of India,” has been particularly affected. Both floods and waterlogging have crippled agriculture. The monsoon began on June 16, and by the end of September, the state had received 119% of its average rainfall — 44.2 inches instead of the expected 37 inches, a 7.2-inch surplus.
In the Bundelkhand region, which spans parts of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, July’s rainfall broke a ten-year record. Sagar district recorded 471 mm, Tikamgarh 416 mm, Damoh 365 mm, Niwari 362 mm, and Chhatarpur 261 mm. The rain persisted through October, flooding villages and turning agricultural land into temporary lakes. Bundelkhand, already known for its fragile ecology and dependence on monsoon rains, saw crops submerged instead of nourished. The result: massive losses of yield and income.

The ground reality: Voices from the fields
A glimpse of the devastation can be seen in the rural belt of Sagar district, where a majority of the population depends on agriculture. Kesli Tehsil, located about 65 km from Sagar city, is known for its fertile soil and green cover. But this year, the sight is heartbreaking — bent paddy stalks, rotting soybean pods, and maize that never reached maturity.
“Even clearing the field costs more than what we’ll earn.” In Chirai village, farmers are counting their losses. Arjun, a natural farming practitioner who owns about 12 acres, says, “Agriculture is the livelihood for all communities here — Brahmin, Thakur, Adivasi, Harijan, and Chadhar. The rains destroyed everyone’s crops. Even the ‘murum’ (gravelly) soil areas are damaged, and crops on black and yellow soil have been wiped out. Until July–August, everything looked promising. Then the rain washed away the crops — and our hopes. The damage is so severe that we won’t even recover the cost of clearing the fields. Farmers will now have to borrow money for the next crop. I fear many small farmers will leave their fields unsown.”

He paused before adding, “A farmer’s income mainly depends on two or three crops a year. Money comes only when we sell them. If the crops are ruined, how will we survive?”
“Our maize only grew three feet”

Sachin Thakur, another farmer from Chirai with 15 acres of land, shares, “I sowed soybean and maize. The soybean was mostly spoiled by the rain, and what remained dried up. The maize plants only grew three to four feet. Some cobs developed, but most plants had none, and the few cobs that did grow had fewer kernels. Nearby villages like Jaruwa, Bamni, Patna, Samnapur, Kukwara, and Mahka are all suffering the same fate.”
“The biodiversity of our fields is dying”
Ramji Thakur, also from Chirai and a member of the Bharatiya Kisan Sangh (Indian Farmers’ Union), explains: “We five brothers cultivate about 40 acres. This year we sowed maize, paddy, and soybean. All have been hit badly. The soybean is completely ruined — we’ll have to plough it back into the soil. Apart from the rain, the biodiversity of our crops and fields is also in danger. The government must take steps for conservation, inspection, and field development to preserve soil fertility and crop purity.”
“Only a little hope left for maize”
In Utkata village, Suresh Kumar Mehra manages 12 acres (four owned, eight leased).
“I planted radish, sponge gourd, pigeon pea (tur), groundnut, and maize. Except for maize on two acres, everything was destroyed by rain and waterlogging. Only the maize gives me a little hope.”

“A fungus ruined our maize”
From Jetpur Doma village, Sitaram Patel says, “I have six acres, and my family has been farming for three generations. This time we grew bottle gourd and tomato, which survived. But maize around us is ruined. About 10% of it got a fungal disease because of waterlogging. The plants couldn’t withstand the rain.”
“Rs 40,000 gone—and nothing to show for it”

Govind Patel from Chauka village detailed his financial losses, “I sowed maize and pigeon pea on five acres. I spent around Rs 40,000 (approx. $480) on seeds, fertilizer, and chemicals. The pigeon pea is completely gone. Only maize might help me recover part of the cost. But most farmers nearby have maize that only grew two to two-and-a-half feet before turning yellow.”
“Only a third of our seeds sprouted”
Ajab Singh, a farmer from Kewlari Kalan, shares, “Here we have small and big farmers, and everyone’s crop is affected. We sowed paddy, soybean, and maize, but because of continuous rain and waterlogging, many seeds didn’t even sprout. In most fields, only about 25–30% of the seeds grew.”
He added that crops in surrounding villages like Kheri, Semra, Ghana, and Idalpur were also submerged.
“In low-lying areas, 90% of crops are gone”

Arvind Bhaiji, another Kesli farmer, says, “The flat and low-lying fields are more damaged, while crops in slightly elevated areas are better. Some crops are 50% damaged, others 70%, and some even 90% ruined. The rain caused root rot, and the urea fertilizer has been washed away. Farmers here have small landholdings and little money to manage rainwater.”
District Farmers’ Union: ‘Satellite surveys can’t see reality’
When contacted, Raghuvir Tomar, district president of the Bharatiya Kisan Sangh, says, “the situation of both crops and farmers is very bad. We are demanding that the government conduct an accurate survey and give compensation.”
He criticized the current assessment methods, “In some places, a satellite survey is being used, but it’s not accurate. It doesn’t show the condition of the kernels or the extent of the rot. The ground reality is much worse.”
Climate Change, adaptation, and farmer-led Solutions
As farmers struggle to rebuild, Akash Chaurasia, a nationally recognized innovator in sustainable agriculture, offers a hopeful path. Known for developing Multi-Layer Farming, Akash believes the situation is not hopeless — it just demands adaptation.

“This imbalance of excessive rain is a form of climate change,” he explains. “It’s a disruption that can destroy ecosystems if farmers don’t adapt. But solutions exist.”
His advice is straightforward and affordable:
1. Build Drainage Channels
“During heavy rain, farmers should dig a two-foot-deep and two-foot-wide drain around the raised boundary (med) of their field. This helps excess water escape into canals or pits. When water collects underground, it recharges groundwater and prevents soil erosion. Fertilizer won’t wash away, and waterlogging will end.”
2. Adopt Raised-Bed (Med) Sowing
“In the Med method, crops are sown four to five inches above the ground. When it rains, the water stays in the drains, not around the crop. This prevents root rot. Farmers can do this with their own labour — no extra money is needed. I’ve used it on my own farm, and our crops stay healthy even in heavy rain.”
Akash believes such simple practices, if widely adopted, could transform India’s vulnerability into resilience.
“If every farmer in waterlogged regions followed these two steps, we could save thousands of acres every year.”

Government Support — And What’s Still Missing
India has several schemes designed to protect farmers from disasters:
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (2016): Provides crop insurance and financial assistance during natural calamities.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana (PM-KISAN, 2019): Offers Rs 6,000 (approx. $72) annually to farmers for basic support.
- Mukhyamantri Kisan Kalyan Yojana (2020): Adds another Rs 6,000 (approx. $72) per year from the state government.
Despite these, many farmers say the support arrives late or doesn’t cover losses. As Arjun pointed out, “We can’t wait months for relief when we have to buy seeds next week.”
Experts argue that while insurance and compensation help recovery, the real solution lies in prevention — teaching farmers low-cost water management, soil conservation, and climate-resilient methods.
Bringing science and policy Together
Agricultural scientists emphasize the importance of integrating climate-adaptive strategies into local farming practices. Soil moisture mapping, satellite-assisted flood prediction, and localized extension services can inform when to sow, which crops to prioritize, and how to manage water in extreme rainfall years.
What the farmers of Bundelkhand need is not just relief but resilience. Drainage systems, raised-bed cultivation, and better soil management can all help farmers cope with erratic rainfall
Bundelkhand’s case demonstrates a broader climate reality: traditional monsoon patterns no longer guarantee stable farming. What worked decades ago may fail today. Farmers, government agencies, and scientific institutions must collaborate to create resilient systems that protect crops, livelihoods, and the environment.
What the farmers of Bundelkhand need is not just relief but resilience. Drainage systems, raised-bed cultivation, and better soil management can all help farmers cope with erratic rainfall. Local governments could play a transformative role by integrating these ideas into training programs, agricultural extension services, and climate adaptation schemes.
The story of this year’s rain in Madhya Pradesh is one of loss — but also of learning. Farmers like Akash Chaurasia show that adaptation begins with awareness and small, practical steps. If those lessons spread across India’s rural heartland, future monsoons might once again bring prosperity, not panic. The monsoon, once India’s lifeline, is now becoming unpredictable under a changing climate. What farmers in Madhya Pradesh need most is not just compensation—but climate-smart solutions that can secure their future harvests.
(The story is part of EdPublica’s Solutions Journalism Initiative)
-

 Space & Physics5 months ago
Space & Physics5 months agoIs Time Travel Possible? Exploring the Science Behind the Concept
-

 Earth6 months ago
Earth6 months ago122 Forests, 3.2 Million Trees: How One Man Built the World’s Largest Miyawaki Forest
-

 Space & Physics6 months ago
Space & Physics6 months agoDid JWST detect “signs of life” in an alien planet?
-

 Know The Scientist5 months ago
Know The Scientist5 months agoNarlikar – the rare Indian scientist who penned short stories
-

 Society4 months ago
Society4 months agoShukla is now India’s first astronaut in decades to visit outer space
-

 Society4 months ago
Society4 months agoAxiom-4 will see an Indian astronaut depart for outer space after 41 years
-

 Earth4 months ago
Earth4 months agoWorld Environment Day 2025: “Beating plastic pollution”
-

 Society6 months ago
Society6 months agoRabies, Bites, and Policy Gaps: One Woman’s Humane Fight for Kerala’s Stray Dogs