Space & Physics
New antenna design could help detect faint cosmological signals
This could revolutionise our ability to detect the faint signals of Cosmological Recombination Radiation (CRR)

In an intriguing development, scientists at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in Bangalore, India, have developed a novel antenna design that could revolutionise our ability to detect the faint signals of Cosmological Recombination Radiation (CRR).
These signals, which are crucial for understanding the thermal and ionization history of the Universe, have so far remained undetected due to their elusive nature. The newly designed antenna is capable of measuring signals in the 2.5 to 4 Gigahertz (GHz) frequency range, which is optimal for detecting CRR, a signal that is approximately one billion times fainter than the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB).
As per available sources, the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old, and in its earliest stages, it was extremely hot and dense. During this time, the Universe was composed of a plasma of free electrons, protons, and light nuclei such as helium and lithium. The radiation coexisting with this matter has been detected today as the CMB, which holds vital information about the early cosmological and astrophysical processes.
One such process, known as the Epoch of Recombination, marks the transition from a fully ionized primordial plasma to mostly neutral hydrogen and helium atoms. This transition emitted photons, creating the Cosmological Recombination Radiation (CRR), which distorts the underlying CMB spectrum. Detecting these faint CRR signals would provide a wealth of information about the Universe’s early ionization and thermal history and could even offer the first experimental measurements of helium abundance before it was synthesized in the cores of stars.
However, detecting CRR is a significant challenge because these signals are extremely weak—about nine orders of magnitude fainter than the CMB. To address this, scientists need highly sensitive instruments that can isolate these signals from the vast cosmic noise surrounding them.
To this end, researchers from RRI, including Mayuri Rao and Keerthipriya Sathish, along with Debdeep Sarkar from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have developed an innovative ground-based broadband antenna designed to detect signals as faint as one part in 10,000. Their design is capable of making sky measurements in the 2.5 to 4 GHz range, the frequency band most suitable for CRR detection.
According to Keerthipriya Sathish, the lead author of the study, “For the sky measurements we plan to perform, this broadband antenna offers the highest sensitivity compared to other antennas designed for the same bandwidth. The antenna’s frequency-independent performance across a wide range and its smooth frequency response are features that set it apart from conventional designs.”
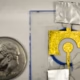
The antenna is compact and lightweight, weighing just 150 grams, with a square shape measuring 14 cm by 14 cm.
The proposed antenna is a dual-polarized dipole antenna with a unique four-arm structure shaped like a fantail. This design ensures that the antenna maintains the same radiation pattern across its entire operational bandwidth, with a mere 1% variation in its characteristics. This is crucial for distinguishing spectral distortions from galactic foregrounds. The antenna’s custom design allows it to “stare” at the same patch of sky throughout its full operational range of 1.5 GHz (from 2.5 to 4 GHz), which is key to separating the CRR signals from other cosmic noise.
The antenna is compact and lightweight, weighing just 150 grams, with a square shape measuring 14 cm by 14 cm. It is made using a low-loss dielectric flat substrate on which the antenna is etched in copper, while the bottom features an aluminum ground plate. Between these plates lies a radio-transparent foam layer that houses the antenna’s connectors and receiver base.
With a sensitivity of around 30 millikelvin (mK) across the 2.5-4 GHz frequency range, the antenna is capable of detecting tiny temperature variations in the sky. Even before being scaled to a full array, this antenna design is expected to provide valuable first scientific results when integrated with a custom receiver. One of the anticipated experiments is to study an excess radiation reported at 3.3 GHz, which has been speculated to result from exotic phenomena, including dark matter annihilation. These early tests will help refine the antenna’s performance and guide future design improvements aimed at achieving the sensitivity required for CRR detection.
The researchers plan to deploy an array of these antennas in radio-quiet areas, where radio frequency interference is minimal or absent. The antenna’s design is straightforward and can be easily fabricated using methods similar to those employed in Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing, ensuring high machining accuracy and consistency for scaling up to multiple-element arrays. The antenna is portable, making it easy to deploy in remote locations for scientific observations.
The team is already looking ahead, planning further improvements to achieve even greater sensitivity, with a long-term goal of detecting CRR signals at sensitivities as low as one part per billion. With this innovative antenna design, the team hopes to make significant strides toward uncovering the secrets of the early Universe and its formation.
Space & Physics
MIT unveils an ultra-efficient 5G receiver that may supercharge future smart devices
A key innovation lies in the chip’s clever use of a phenomenon called the Miller effect, which allows small capacitors to perform like larger ones

A team of MIT researchers has developed a groundbreaking wireless receiver that could transform the future of Internet of Things (IoT) devices by dramatically improving energy efficiency and resilience to signal interference.
Designed for use in compact, battery-powered smart gadgets—like health monitors, environmental sensors, and industrial trackers—the new chip consumes less than a milliwatt of power and is roughly 30 times more resistant to certain types of interference than conventional receivers.
“This receiver could help expand the capabilities of IoT gadgets,” said Soroush Araei, an electrical engineering graduate student at MIT and lead author of the study, in a media statement. “Devices could become smaller, last longer on a battery, and work more reliably in crowded wireless environments like factory floors or smart cities.”
The chip, recently unveiled at the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, stands out for its novel use of passive filtering and ultra-small capacitors controlled by tiny switches. These switches require far less power than those typically found in existing IoT receivers.
A key innovation lies in the chip’s clever use of a phenomenon called the Miller effect, which allows small capacitors to perform like larger ones. This means the receiver achieves necessary filtering without relying on bulky components, keeping the circuit size under 0.05 square millimeters.
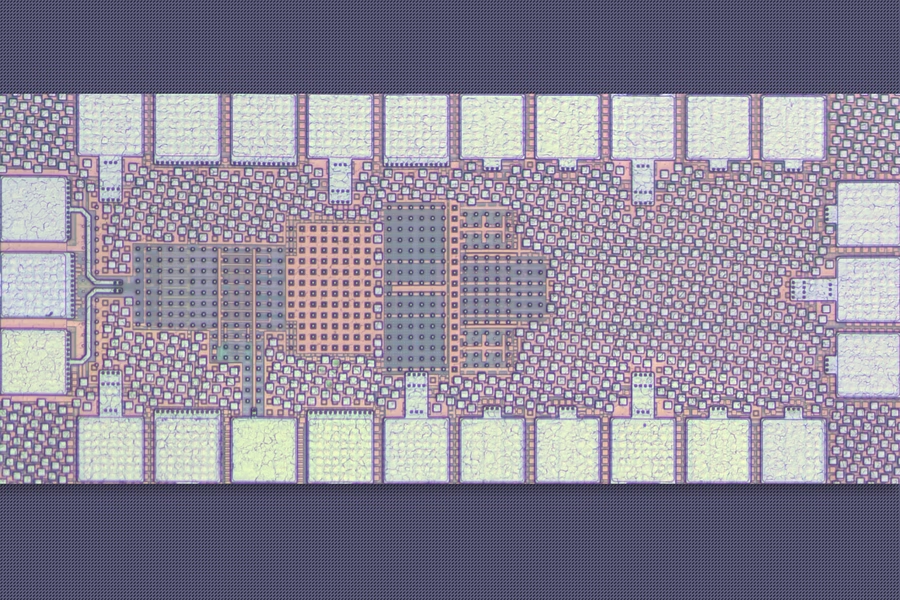
Traditional IoT receivers rely on fixed-frequency filters to block interference, but next-generation 5G-compatible devices need to operate across wider frequency ranges. The MIT design meets this demand using an innovative on-chip switch-capacitor network that blocks unwanted harmonic interference early in the signal chain—before it gets amplified and digitized.
Another critical breakthrough is a technique called bootstrap clocking, which ensures the miniature switches operate correctly even at a low power supply of just 0.6 volts. This helps maintain reliability without adding complex circuitry or draining battery life.
The chip’s minimalist design—using fewer and smaller components—also reduces signal leakage and manufacturing costs, making it well-suited for mass production.
Looking ahead, the MIT team is exploring ways to run the receiver without any dedicated power source—possibly by harvesting ambient energy from nearby Wi-Fi or Bluetooth signals.
The research was conducted by Araei alongside Mohammad Barzgari, Haibo Yang, and senior author Professor Negar Reiskarimian of MIT’s Microsystems Technology Laboratories.
Society
Ahmedabad Plane Crash: The Science Behind Aircraft Take-Off -Understanding the Physics of Flight
Take-off is one of the most critical phases of flight, relying on the precise orchestration of aerodynamics, propulsion, and control systems. Here’s how it works:

On June 12, 2025, a tragic aviation accident struck Ahmedabad, India when a regional passenger aircraft, Air India flight A1-171, crashed during take-off at Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport. According to preliminary reports, the incident resulted in over 200 confirmed casualties, including both passengers and crew members, and several others are critically injured. The aviation community and scientific world now turn their eyes not just toward the cause but also toward understanding the complex science behind what should have been a routine take-off.
How Do Aircraft Take Off?
Take-off is one of the most critical phases of flight, relying on the precise orchestration of aerodynamics, propulsion, and control systems. Here’s how it works:
1. Lift and Thrust
To leave the ground, an aircraft must generate lift, a force that counters gravity. This is achieved through the unique shape of the wing, called an airfoil, which creates a pressure difference — higher pressure under the wing and lower pressure above — according to Bernoulli’s Principle and Newton’s Third Law.
Simultaneously, engines provide thrust, propelling the aircraft forward. Most commercial jets use turbofan engines, which accelerate air through turbines to generate power.
2. Critical Speeds
Before takeoff, pilots calculate critical speeds:
- V1 (Decision Speed): The last moment a takeoff can be safely aborted.
- Vr (Rotation Speed): The speed at which the pilot begins to lift the nose.
- V2 (Takeoff Safety Speed): The speed needed to climb safely even if one engine fails.
If anything disrupts this process — like bird strikes, engine failure, or runway obstructions — the results can be catastrophic.

Environmental and Mechanical Challenges
Factors like wind shear, runway surface condition, mechanical integrity, or pilot error can interfere with safe take-off. Investigators will be analyzing these very aspects in the Ahmedabad case.
The Bigger Picture
Take-off accounts for a small fraction of total flight time but is disproportionately associated with accidents — approximately 14% of all aviation accidents occur during take-off or initial climb.
Space & Physics
MIT claims breakthrough in simulating physics of squishy, elastic materials
In a series of experiments, the new solver demonstrated its ability to simulate a diverse array of elastic behaviors, ranging from bouncing geometric shapes to soft, squishy characters

Researchers at MIT claim to have unveiled a novel physics-based simulation method that significantly improves stability and accuracy when modeling elastic materials — a key development for industries spanning animation, engineering, and digital fabrication.
In a series of experiments, the new solver demonstrated its ability to simulate a diverse array of elastic behaviors, ranging from bouncing geometric shapes to soft, squishy characters. Crucially, it maintained important physical properties and remained stable over long periods of time — an area where many existing methods falter.
Other simulation techniques frequently struggled in tests: some became unstable and caused erratic behavior, while others introduced excessive damping that distorted the motion. In contrast, the new method preserved elasticity without compromising reliability.
“Because our method demonstrates more stability, it can give animators more reliability and confidence when simulating anything elastic, whether it’s something from the real world or even something completely imaginary,” Leticia Mattos Da Silva, a graduate student at MIT’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, said in a media statement.
Their study, though not yet peer-reviewed or published, will be presented at the August proceedings of the SIGGRAPH conference in Vancouver, Canada.
While the solver does not prioritize speed as aggressively as some tools, it avoids the accuracy and robustness trade-offs often associated with faster methods. It also sidesteps the complexity of nonlinear solvers, which are commonly used in physics-based approaches but are often sensitive and prone to failure.
Looking ahead, the research team aims to reduce computational costs and broaden the solver’s applications. One promising direction is in engineering and fabrication, where accurate elastic simulations could enhance the design of real-world products such as garments, medical devices, and toys.
“We were able to revive an old class of integrators in our work. My guess is there are other examples where researchers can revisit a problem to find a hidden convexity structure that could offer a lot of advantages,” Mattos Da Silva added.
The study opens new possibilities not only for digital content creation but also for practical design fields that rely on predictive simulations of flexible materials.
-

 Society4 months ago
Society4 months agoStarliner crew challenge rhetoric, says they were never “stranded”
-

 Space & Physics3 months ago
Space & Physics3 months agoCould dark energy be a trick played by time?
-

 Earth4 months ago
Earth4 months agoHow IIT Kanpur is Paving the Way for a Solar-Powered Future in India’s Energy Transition
-

 Space & Physics3 months ago
Space & Physics3 months agoSunita Williams aged less in space due to time dilation
-

 Learning & Teaching5 months ago
Learning & Teaching5 months agoCanine Cognitive Abilities: Memory, Intelligence, and Human Interaction
-

 Earth3 months ago
Earth3 months ago122 Forests, 3.2 Million Trees: How One Man Built the World’s Largest Miyawaki Forest
-

 Women In Science3 months ago
Women In Science3 months agoNeena Gupta: Shaping the Future of Algebraic Geometry
-

 Society5 months ago
Society5 months agoSustainable Farming: The Microgreens Model from Kerala, South India