The Sciences
Researchers develop AI algorithm to accurately detect heart murmurs in dogs
Researchers have developed AI Algorithm to detect heart murmurs in dogs, improving early diagnosis of cardiac disease

Researchers at the University of Cambridge have developed a machine learning algorithm capable of accurately detecting heart murmurs in dogs—a critical indicator of cardiac disease, particularly prevalent in smaller breeds like the King Charles Spaniel. This innovative approach has the potential to transform veterinary care, offering an accessible tool for early diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions.
Heart murmurs are a key sign of mitral valve disease, the most common heart issue affecting adult dogs. Statistically, approximately one in every 30 dogs seen by a veterinarian presents with a heart murmur, with higher rates observed in small breeds and older dogs. Given the frequency of such conditions, timely detection is essential. Early intervention can significantly enhance a dog’s quality of life and longevity, making effective screening methods vital for veterinarians.
Dr. Andrew McDonald, the study’s first author from the Department of Engineering at Cambridge, emphasized the importance of early detection, according to a statement issued by the University: “Heart disease in humans is a huge health issue, but in dogs it’s an even bigger problem. Most smaller dog breeds will have heart disease when they get older, but obviously dogs can’t communicate in the same way that humans can, so it’s up to primary care vets to detect heart disease early enough so it can be treated.”
The Algorithm’s Development
The research team began with an algorithm initially designed for human heart sound analysis. Recognizing the similarities between mammalian heart function, they adapted this technology to analyze audio recordings from digital stethoscopes used on dogs. The algorithm demonstrated an impressive sensitivity of 90% in detecting heart murmurs, a level of accuracy comparable to that of expert cardiologists.
Professor Anurag Agarwal, the lead researcher and an expert in acoustics and bioengineering, noted the absence of a dedicated database for canine heart sounds. “As far as we’re aware, there are no existing databases of heart sounds in dogs, which is why we started out with a database of heart sounds in humans,” he explained in a statement issued by the University of Cambridge. “Mammalian hearts are fairly similar, and when things go wrong, they tend to go wrong in similar ways.”
The team refined the algorithm to not only detect but also grade heart murmurs
To build a robust dataset, the researchers collected heart sound data from nearly 800 dogs undergoing routine examinations at four veterinary specialist centers across the UK. Each dog received a thorough physical examination and an echocardiogram performed by a cardiologist, who graded any detected murmurs and identified underlying cardiac issues. This effort resulted in the largest dataset of dog heart sounds ever compiled.
Expanding the Dataset for Better Outcomes
Co-author Professor Jose Novo Matos, a small animal cardiology specialist, highlighted the need for diverse data to improve the algorithm’s effectiveness: “Mitral valve disease mainly affects smaller dogs, but to test and improve our algorithm, we wanted to get data from dogs of all shapes, sizes, and ages. The more data we have to train it, the more useful our algorithm will be, both for vets and for dog owners.”
The team refined the algorithm to not only detect but also grade heart murmurs, distinguishing between mild and advanced disease requiring further intervention. This innovation aims to empower general veterinarians, reducing the need for expensive specialized scans and consultations with cardiologists.
Promising Results and Future Implications
The algorithm’s performance was encouraging: it aligned with cardiologists’ assessments in over half of the cases, and in 90% of instances, it was within one grading unit of the cardiologist’s evaluation. Dr. McDonald pointed out the practical implications of these findings: “The grade of heart murmur is a useful differentiator for determining next steps and treatments, and we’ve automated that process.”
Novo Matos remarked on the transformative potential of this technology, seeing it as a supportive tool rather than a job threat. “So many people talk about AI as a threat to jobs, but for me, I see it as a tool that will make me a better cardiologist,” he said. With the veterinary profession facing time constraints and a shortage of specialists, this algorithm could streamline the process of identifying dogs that need urgent care.
A Path Forward for Veterinary Medicine
The researchers’ ultimate goal is to equip veterinarians with the means to make informed decisions regarding treatment, enhancing the quality of life for their canine patients. “Knowing when to medicate is so important, in order to give dogs the best quality of life possible for as long as possible,” said Agarwal.
Supported by organisations such as the Kennel Club Charitable Trust and the Medical Research Council, this research marks a significant step forward in the use of machine learning for veterinary applications. As technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of not only advancing animal health but also improving the human-animal bond through better care and understanding.
The Sciences
Most Earthquake Energy Is Spent Heating Up Rocks, Not Shaking the Ground: New MIT Study Finds
How do earthquakes spend their energy? MIT’s latest research shows heat—not ground motion—is the main outcome of a quake, reshaping how scientists understand seismic risks
When an earthquake strikes, we experience its violent shaking on the surface. But new research from MIT shows that most of a quake’s energy actually goes into something entirely different — heat.
Using miniature “lab quakes” designed to mimic real seismic slips deep underground, geologists at MIT have, for the first time, mapped the full energy budget of an earthquake. Their study reveals that only about 10 percent of a quake’s energy translates into ground shaking, while less than 1 percent goes into fracturing rock. The vast majority — nearly 80 percent — is released as heat at the fault, sometimes creating sudden spikes hot enough to melt surrounding rock.
“These results show that what happens deep underground is far more dynamic than what we feel on the surface,” said Daniel Ortega-Arroyo, a graduate researcher in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, in a media statement. “A rock’s deformation history — essentially its memory of past seismic shifts — dictates how much energy ends up in shaking, breaking, or heating. That history plays a big role in determining how destructive a quake can be.”
The team’s findings, published in AGU Advances, suggest that understanding a fault zone’s “thermal footprint” might be just as important as recording surface tremors. Laboratory-created earthquakes, though simplified models of natural ones, provide a rare window into processes that are otherwise impossible to observe deep within Earth’s crust.
MIT researchers created the “microshakes” by applying immense pressures to samples of granite mixed with magnetic particles that acted as ultra-sensitive heat gauges. By stacking the results of countless tiny quakes, they tracked exactly how the energy distributed among shaking, fracturing, and heating. Some events saw fault zones heat up to over 1,200 degrees Celsius in mere microseconds, momentarily liquefying parts of the rock before cooling again.
“We could never reproduce the full complexity of Earth, so we simplify,” explained co-author Matěj Peč, MIT associate professor of geophysics. “By isolating the physics in the lab, we can begin to understand the mechanisms that govern real earthquakes — and apply this knowledge to better models and risk assessments.”
The work also provides a fresh perspective on why some regions remain vulnerable long after previous seismic activity. Past quakes, by altering the structure and material properties of rocks, may influence how future ones unfold. If researchers can estimate how much heat was generated in past quakes, they might be able to assess how much stress still lingers underground — a factor that could refine earthquake forecasting.
The study was conducted by Ortega-Arroyo and Peč, along with colleagues from MIT, Harvard University, and Utrecht University.
Health
Giant Human Antibody Found to Act Like a Brace Against Bacterial Toxins
This synergistic bracing action gives IgM a unique advantage in neutralizing bacterial toxins that are exposed to mechanical forces inside the body
Our immune system’s largest antibody, IgM, has revealed a hidden superpower — it doesn’t just latch onto harmful microbes, it can also act like a brace, mechanically stabilizing bacterial toxins and stopping them from wreaking havoc inside our bodies.
A team of scientists from the S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS) in Kolkata, India, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), made this discovery in a recent study. The team reports that IgM can mechanically stiffen bacterial proteins, preventing them from unfolding or losing shape under physical stress.
“This changes the way we think about antibodies,” the researchers said in a media statement. “Traditionally, antibodies are seen as chemical keys that unlock and disable pathogens. But we show they can also serve as mechanical engineers, altering the physical properties of proteins to protect human cells.”
Unlocking a new antibody role
Our immune system produces many different antibodies, each with a distinct function. IgM, the largest and one of the very first antibodies generated when our body detects an infection, has long been recognized for its front-line defense role. But until now, little was known about its ability to physically stabilize dangerous bacterial proteins.
The SNBNCBS study focused on Protein L, a molecule produced by Finegoldia magna. This bacterium is generally harmless but can become pathogenic in certain situations. Protein L acts as a “superantigen,” binding to parts of antibodies in unusual ways and interfering with immune responses.
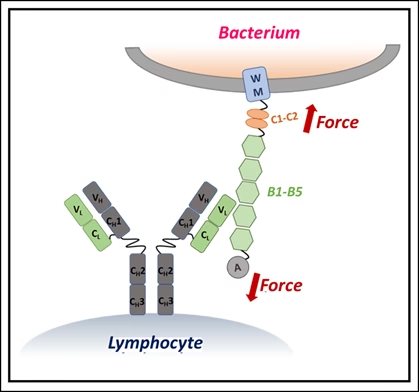
Using single-molecule force spectroscopy — a high-precision method that applies minuscule forces to individual molecules — the researchers discovered that when IgM binds Protein L, the bacterial protein becomes more resistant to mechanical stress. In effect, IgM braces the molecule, preventing it from unfolding under physiological forces, such as those exerted by blood flow or immune cell pressure.
Why size matters
The stabilizing effect depended on IgM concentration: more IgM meant stronger resistance. Simulations showed that this is because IgM’s large structure carries multiple binding sites, allowing it to clamp onto Protein L at several locations simultaneously. Smaller antibodies lack this kind of stabilizing network.
“This synergistic bracing action gives IgM a unique advantage in neutralizing bacterial toxins that are exposed to mechanical forces inside the body,” the researchers explained.
The finding highlights an overlooked dimension of how our immune system works — antibodies don’t merely bind chemically but can also act as mechanical modulators, physically disarming toxins.
Such insights could open a new frontier in drug development, where future therapies may involve engineering antibodies to stiffen harmful proteins, effectively locking them in a harmless state.
The study suggests that by harnessing this natural bracing mechanism, scientists may be able to design innovative treatments that go beyond traditional antibody functions.
Math
Researchers Unveil Breakthrough in Efficient Machine Learning with Symmetric Data

MIT researchers have developed the first mathematically proven method for training machine learning models that can efficiently interpret symmetric data—an advance that could significantly enhance the accuracy and speed of AI systems in fields ranging from drug discovery to climate analysis.
In traditional drug discovery, for example, a human looking at a rotated image of a molecule can easily recognize it as the same compound. However, standard machine learning models may misclassify the rotated image as a completely new molecule, highlighting a blind spot in current AI approaches. This shortcoming stems from the concept of symmetry, where an object’s fundamental properties remain unchanged even when it undergoes transformations like rotation.
“If a drug discovery model doesn’t understand symmetry, it could make inaccurate predictions about molecular properties,” the researchers explained. While some empirical techniques have shown promise, there was previously no provably efficient way to train models that rigorously account for symmetry—until now.
“These symmetries are important because they are some sort of information that nature is telling us about the data, and we should take it into account in our machine-learning models. We’ve now shown that it is possible to do machine-learning with symmetric data in an efficient way,” said Behrooz Tahmasebi, MIT graduate student and co-lead author of the new study, in a media statement.
The research, recently presented at the International Conference on Machine Learning, is co-authored by fellow MIT graduate student Ashkan Soleymani (co-lead author), Stefanie Jegelka (associate professor of EECS, IDSS member, and CSAIL member), and Patrick Jaillet (Dugald C. Jackson Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and principal investigator at LIDS).
Rethinking how AI sees the world
Symmetric data appears across numerous scientific disciplines. For instance, a model capable of recognizing an object irrespective of its position in an image demonstrates such symmetry. Without built-in mechanisms to process these patterns, machine learning models can make more mistakes and require massive datasets for training. Conversely, models that leverage symmetry can work faster and with fewer data points.
“Graph neural networks are fast and efficient, and they take care of symmetry quite well, but nobody really knows what these models are learning or why they work. Understanding GNNs is a main motivation of our work, so we started with a theoretical evaluation of what happens when data are symmetric,” Tahmasebi noted.
The MIT researchers explored the trade-off between how much data a model needs and the computational effort required. Their resulting algorithm brings symmetry to the fore, allowing models to learn from fewer examples without spending excessive computing resources.
Blending algebra and geometry
The team combined strategies from both algebra and geometry, reformulating the problem so the machine learning model could efficiently process the inherent symmetries in the data. This innovative blend results in an optimization problem that is computationally tractable and requires fewer training samples.
“Most of the theory and applications were focusing on either algebra or geometry. Here we just combined them,” explained Tahmasebi.
By demonstrating that symmetry-aware training can be both accurate and efficient, the breakthrough paves the way for the next generation of neural network architectures, which promise to be more precise and less resource-intensive than conventional models.
“Once we know that better, we can design more interpretable, more robust, and more efficient neural network architectures,” added Soleymani.
This foundational advance is expected to influence future research in diverse applications, including materials science, astronomy, and climate modeling, wherever symmetry in data is a key feature.

 Space & Physics5 months ago
Space & Physics5 months agoIs Time Travel Possible? Exploring the Science Behind the Concept

 Know The Scientist5 months ago
Know The Scientist5 months agoNarlikar – the rare Indian scientist who penned short stories

 Society4 months ago
Society4 months agoShukla is now India’s first astronaut in decades to visit outer space

 Earth5 months ago
Earth5 months agoWorld Environment Day 2025: “Beating plastic pollution”

 Society5 months ago
Society5 months agoAxiom-4 will see an Indian astronaut depart for outer space after 41 years

 The Sciences4 months ago
The Sciences4 months agoHow a Human-Inspired Algorithm Is Revolutionizing Machine Repair Models in the Wake of Global Disruptions

 Space & Physics3 months ago
Space & Physics3 months agoJoint NASA-ISRO radar satellite is the most powerful built to date

 Space & Physics6 months ago
Space & Physics6 months agoMIT Physicists Capture First-Ever Images of Freely Interacting Atoms in Space