Society
Why mother language-based science education is essential
All people are touched by science; shouldn’t that be universally understood? Shouldn’t everyone take part in this?
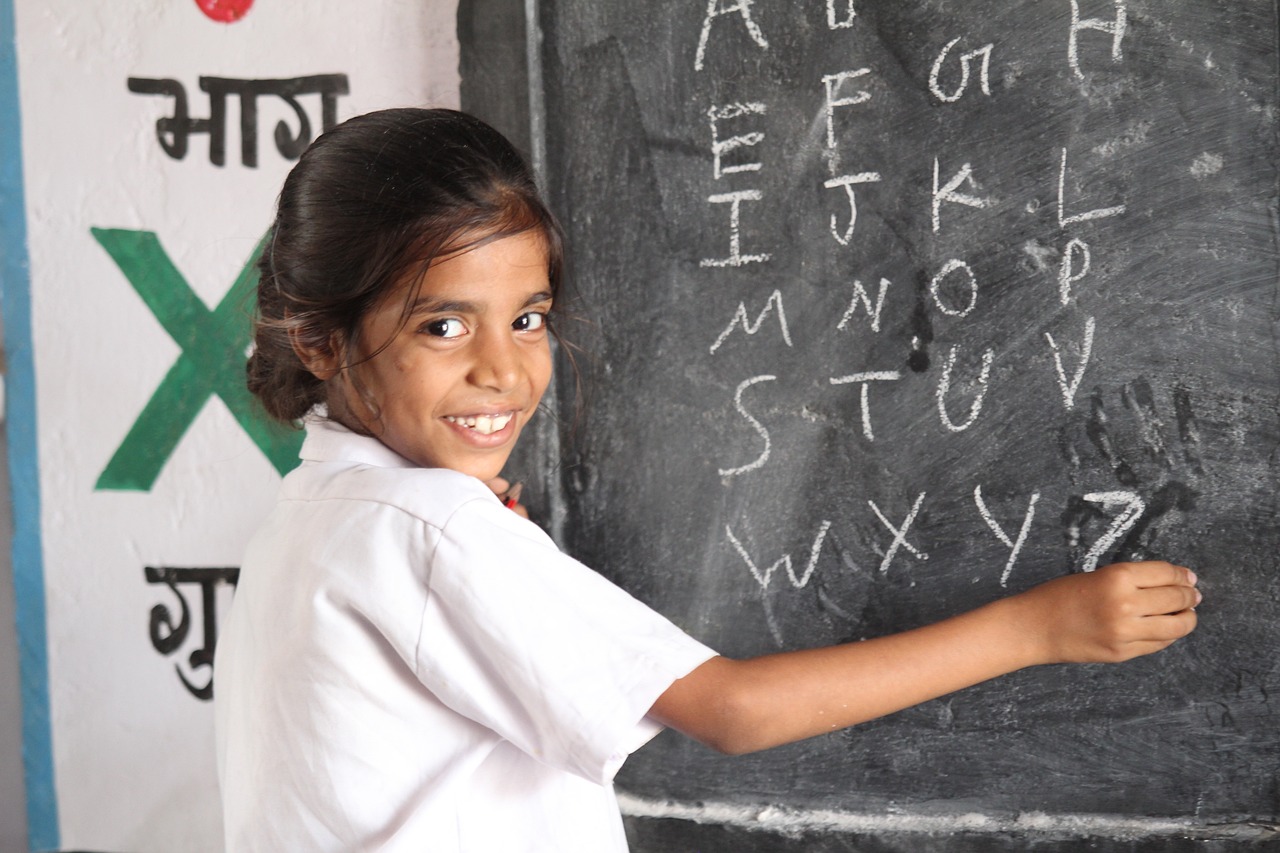
EdPublica looks into the importance of mother language-based science education in the context of International Mother Language Day on February 21. We believe that the global fabric of linguistic diversity is facing a growing threat with the rapid disappearance of numerous languages over time.
Science is not democratic; it is an elitist activity…an Indian theoretical physicist once said. He means that science is not that democratic, so everyone does not need to learn, only the elite should learn. Does it make sense? All people are touched by science; shouldn’t that be universally understood? Shouldn’t everyone take part in this?
It should, but one big barrier is the language itself. Further democratising science education in the mother tongue will make this difficult topic more accessible to all.
The setting was a typical English-medium school in a rural village in the South Indian state of Kerala. The teacher seemed to be taking classes for 6th or 7th graders. She was reading the book in English without missing a single line. The teacher was very excited. However, the children’s body language did not show much enthusiasm. Many students’ expressions were just filled with a sense that they had heard something. The class was about light or something. The subject of the school visit was different, but I just talked to one or two of the children about what they were learning.

One has nothing to say about the rays of light taught by the teacher. They did not like any questions about what was said in class. A boy named Thomas (name changed) said, ‘Oh, I can’t understand any class in English, bro’.
It was a reality that most subjects taught in English were beyond the comprehension of the students there. Then the question is how to pass the examinations. “It’s a matter of just memorising and writing,” replied one of the boys. It was then that I remembered about the discussions of primary education, especially science education, in indigenous languages. Many children who pass with great marks in subjects including science have no understanding of basic science concepts. Those who are not good at memory are quickly labelled as dumb and will be marginalised in schools. This is not an isolated case but a common ‘phenomenon’ in third-world and developing countries where English is not the main language.
So, the question is: If you don’t understand, how can you learn?
The situation is deplorable if we consider how little practice there is in teaching science concepts in the mother language, particularly concerning children’s daily lives. Language is one of the main reasons why children don’t have a scientific approach to anything when they grow up.
India’s former President and eminent scientist, Dr. A P J Abdul Kalam, was once interacting with students at Dharampeeth Science College, Nagpur. The incident happened in 2011 or so. He encountered a question about how science learning can be made more creative. This was his answer: For a quick grasp of science-related concepts and greater creativity, teach children science in their mother language.
The same was repeated by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in January 2018. The Prime Minister said that children should be taught science in their native languages. But how much the country is still succeeding in that is questionable. It is a relief that the new National Education Policy of India is all in that direction, but the fundamental change needs to come in the mindset of parents and teachers.
What do studies say?
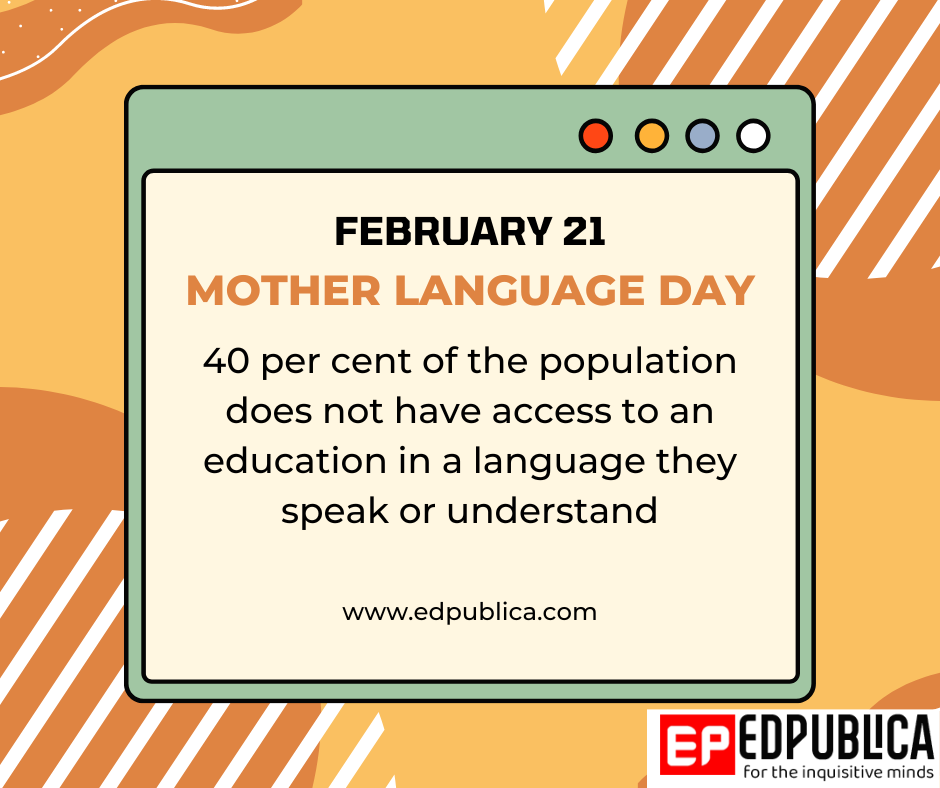
UNESCO’s Global Monitoring Report (GMR) published a landmark study five years ago. It was released on February 21, International Mother Language Day. The study pointed out that providing primary education in a language other than their own can significantly affect the learning process of children.
French is the main language in many West African schools. It is an unfamiliar language to its children. “Naturally, their learning becomes difficult on many levels,” states UNESCO’s policy paper.
As the then UNESCO GMR Director Aaron Benavot told this writer regarding the report, “40 percent of the world’s population does not have access to education in a language they speak or understand. Studying in a non-spoken language regularly sets a student back academically. It affects children from low-income families very deeply.”
UNESCO’s report points out that if children understand the medium of learning, their learning will improve. French is the main language in many West African schools. It is an unfamiliar language to its children. “Naturally, their learning becomes difficult on many levels,” states UNESCO’s policy paper. “Language and ethnicity can combine to produce complex patterns of compounded disadvantage. In Peru, the difference in test scores between indigenous and non-indigenous children in grade 2 is sizeable and increasing.”
Why the bilingual model matters
UNESCO states that children have reached better standards in countries where bilingual programmes have been implemented in the education system. By making learning in their mother tongue possible, children can score better in all subjects. Experts such as Aaron Benavot point to Guatemalan and Ethiopian case studies as proof of this. UNESCO studies say that promoting bilingual education is the best way, even if it is a bit expensive. A bilingual education programme with an emphasis on the mother tongue can make a big difference, although it will create complications in matters including teacher recruitment.
At the same time, just because the study is in the mother language does not necessarily mean that the children will have better scientific aptitude. On the other hand, if science is taught in the mother tongue, the chances of gaining expertise in science are very high. This is mentioned in the new education policy of India. The National Education Policy calls for the use of the local language as the medium of study up to grade 5.

Moreover, such a change is essential for the democratisation of science. Celebrated Indian physicist C V Raman once said that science should be taught in the mother tongue if science is not to be confined to the activities of the elite. Science should be accessible to all. Every human life is related to science. If they want to understand it, science must come to them in a language they know.
Our transition must be to schools that teach science in the language that children speak, beyond mere theories, and relate them to their lives on a practical level. Studies have shown that children become more empowered and confident when they learn in their own language. Because the mother tongue is also related to each person’s sense of identity.
Mother Language Day 2024
UNESCO has put forward a theme for International Mother Language Day celebration 2024 – “Multilingual education is a pillar of intergenerational learning”. Currently, 763 million adults lack basic literacy abilities, and 250 million children and young people do not attend school. UNESCO states that multilingual education is a key component of quality learning, and mother tongue education supports learning, literacy and the acquisition of additional languages.
Climate
Could Global Warming Make Greenland, Norway and Sweden Much Colder?
A Nordic Council report warns that global warming could make Norway colder if the Atlantic ocean circulation collapses, triggering severe climate impacts.

Global warming is usually associated with rising temperatures—but a new Nordic report warns it could drive parts of northern Europe into far colder conditions if a major Atlantic ocean current collapses.
Greenland, Norway and Sweden could experience significantly colder climates as the planet warms, according to a new report by the Nordic Council of Ministers that examines the risks linked to a possible collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC).
The report, A Nordic Perspective on AMOC Tipping, brings together the latest scientific evidence on how global warming is slowing the AMOC—one of the world’s largest ocean circulation systems, responsible for transporting heat from the tropics to the North Atlantic. While a full collapse is considered unlikely, the authors warn that it remains possible even at relatively low levels of global warming, with potentially disruptive consequences for northern countries.
The Reversal
If the circulation were to weaken rapidly or cross a tipping point, the report notes, northern Europe could cool sharply even as the rest of the world continues to warm. Such a reversal would have wide-ranging effects on food production, energy systems, infrastructure, and livelihoods across the Nordic region.
“The AMOC is a key part of the climate system for the Nordic region. While the future of the AMOC is uncertain, the potential for a rapid weakening or collapse is a risk we need to take seriously,” said Aleksi Nummelin, Research Professor at the Finnish Meteorological Institute, in a media statement. “This report brings together current scientific knowledge and highlights practical actions for mitigation, monitoring and preparedness.”
A climate paradox
The AMOC plays a central role in maintaining the relatively mild climate of Northern Europe. As global temperatures rise, melting ice from Greenland and increased freshwater input into the North Atlantic are expected to weaken this circulation. According to the report, such changes could reduce heat transport northwards, leading to colder regional conditions—particularly during winter—even under a globally warming climate.
Scientists caution that the impacts would not simply mirror gradual climate change trends. Instead, an AMOC collapse could trigger abrupt and uneven shifts, including expanded sea ice, stronger storms, altered rainfall patterns, and rising sea levels along European coastlines. Some of these impacts would occur regardless of when or how quickly the circulation weakens.
The report also highlights global ripple effects. A slowdown of the AMOC could shift the tropical rain belt southwards, with potentially severe consequences for monsoon-dependent regions such as parts of Africa and South Asia, underscoring that AMOC tipping is not a regional concern alone.
Calls for precaution and preparedness
Given the uncertainty surrounding when—or if—the AMOC might cross a critical threshold, the report urges policymakers to adopt a precautionary approach. It stresses that any additional global warming, and prolonged overshoot of the 1.5°C target, increases the risk of triggering a collapse.
Key recommendations include accelerating emissions reductions, securing long-term funding for ocean observation networks, and developing an early warning system that integrates real-world measurements with climate model simulations. The authors argue that such systems should be embedded directly into policymaking to enable rapid responses.
The report also calls for climate adaptation strategies that account for multiple futures—including scenarios in which parts of Northern Europe cool rather than warm. It emphasises that AMOC collapse should be treated as a real and significant risk, requiring comprehensive risk management frameworks across climate, ocean, and disaster governance.
Science driving policy attention
The findings were developed through the Nordic Tipping Week workshop held in October 2025 in Helsinki and Rovaniemi, bringing together physical oceanographers, climate scientists, and social scientists from across Nordic and international institutions. The initiative was partly motivated by an open letter submitted in 2024 by 44 climate scientists, warning Nordic policymakers that the risks associated with AMOC tipping may have been underestimated.
By consolidating current scientific understanding and translating it into policy-relevant recommendations, the report aims to shift AMOC collapse from a theoretical concern to a concrete risk requiring immediate attention.
Society
Science Is Talking – Why Aren’t We Hearing?
Why the world still struggles to communicate science, and how researchers, journalists, and
institutions can rebuild a broken chain

Have you ever listened to an expert discuss their work and felt like they were speaking a completely different language? You’re not alone. Scientific breakthroughs have the power to shape our health, environment, and future, yet they often remain locked behind a wall of jargon and complexity, failing to reach the public or the policymakers who write our laws.
This communication breakdown creates a “broken chain of knowledge,” with crucial information stuck at its source. The path from a scientific discovery to public understanding and sound policy is fraught with obstacles, from the culture inside the lab to systemic barriers in government.
Let us look at the most significant reasons for this disconnect. By understanding the challenges from the perspectives of scientists, journalists, and policymakers, we can begin to see how we might mend the chain and ensure that knowledge flows to where it’s needed most.

The First Barrier Isn’t a Wall, It’s a Mindset
The communication problem often begins not with external hurdles, but within the culture of science itself. Before a single word is spoken to the public, an internal mindset can prevent scientists from effectively sharing their work. Some researchers operate with what former Indian minister Jairam Ramesh calls a “high pad” mentality, believing their specialized knowledge places them above the need for public engagement.
As Ramesh recently points out at the Science Journalists Conference of India, Ahmedabad University, this attitude is a primary barrier: “Too often I find scientists sitting on a high pad thinking that they have a better knowledge than the rest of the people… they speak in jargon they speak in their own language and they are really appealing to the community and not necessarily to the non-scientific community.”
Dr. Abhijit Majumdar of IIT Bombay acknowledges that scientists are often poor communicators — but he stresses a deeper issue: “Before learning how to communicate, scientists must first appreciate the need to communicate with the general public.” That awareness, he says, is still lacking in many settings. Experts note that this gap persists for two key reasons. The first is mindset: a cultural tendency to work in isolation — an “ivory tower inside their own ego.” The second is Language: after years of specialization, many scientists use technical vocabulary without realizing it’s incomprehensible jargon to outsiders, effectively building a wall where they intend to build a bridge. Overcoming this internal culture is the first step toward unlocking the mutual benefits of communication.

It’s Not ‘Dumbing Down,’ It’s a Two-Way Street
A fundamental misunderstanding of science communication is that it’s simply “dumbing down” complex work; in reality, it is a transformative, two-way exchange that can lead to deeper insights for the researchers themselves.
When scientists are challenged to explain their work to non-experts, they must distill complex ideas to their “’observable conceptual’ level.” This act of translation often forces them to see their own work from a new perspective, uncovering fresh insights. As Dr. Majumdar states, the benefits flow in both directions:
“It’s a two-way street, it is beneficial for the sides if we learn how to communicate.”
Furthermore, this process can generate questions from the public that are “much more superior” to those scientists typically receive from their peers, pushing their research in new and unexpected directions.

A Scientist’s Silence Creates a Vacuum for Misinformation
In our modern digital world, many scientists are hesitant to speak publicly, “scared that one wrong use of the work can be taken out of the context,” potentially leading to professional backlash. While this caution is understandable, it creates a dangerous paradox.
When credible experts stay silent on a complex issue, they create an “information vacuum.” That empty space will not remain empty for long. It is inevitably filled by less informed, less qualified, or even malicious actors eager to become the spokesperson on the topic. The silence of experts, therefore, directly enables the spread of false narratives.
In an era with a “lot of misinformation,” the proactive solution is a strong partnership between cautious, responsible scientists and trusted journalists. This collaboration is the public’s best and most powerful defense against falsehoods.

The System Itself Is Designed to Fail
Even when individual scientists are willing to engage, they are often crushed by systemic and structural barriers. The larger systems governing science and media are frequently not built to support public communication, a problem that is truly global in scope.
Studies reveal a stark reality. Nearly 46% of academics in one study had never communicated their findings beyond peer circles, with 80% citing a lack of time as a major barrier. A global survey of geoscientists found that while 90% believe they have a moral duty to engage, 87% identified a lack of funding as a key obstacle. This isn’t confined to one region; a study in Zimbabwe found nearly half of academics had never shared their research with public audiences.
In India, this is compounded by institutional support that suffers from “irregular funding” and offers little incentive for sustained engagement. Interestingly, a 2020 Pew Research survey found that 75% of Indians believe government investment in science is worthwhile, suggesting a public appetite for knowledge that the system is failing to meet.
Further straining the system is the inherent conflict between the clashing timelines of science and journalism. Science is slow, careful, and methodical, prioritizing peer review and accuracy. The news cycle is instantaneous and reactive, demanding immediate responses for a public hungry for information. This friction between a scientist’s verification process and a journalist’s deadline puts constant stress on the very relationship needed to bridge the knowledge gap.

In Policy, There’s a Structural Wall Between Science and Law
Even when science successfully reaches the public, the final link in the chain—influencing policy—is often completely broken. In India, for instance, Jairam Ramesh describes a profound structural disconnect between the nation’s scientific community and its lawmakers.
He explains that Members of Parliament receive their information almost exclusively from “government bodies” and “ministries,” not from the independent scientific institutions that house the country’s experts. This has led to a glaring absence of science-informed debate on some of the most critical issues facing the nation, including:
- GM crops
- Nuclear policy
- The increasing frequency of landslides and earthquakes
Global warming and its impact on agriculture, health, and energy
To fix this, Ramesh proposes that India’s scientific academies must take a more “active role.” Instead of relying on individuals, these institutions should consolidate a “collective view” from the scientific community and present it directly to legislators, providing an authoritative voice that is much harder for policymakers to ignore.
Building the Bridge, Together
Mending the broken “chain of knowledge” is not a simple task, nor is it the responsibility of a single group. It requires a collaborative effort from scientists who see communication as a duty, journalists who build trust and provide context, and institutions that create systems that reward and support public engagement.
Breaking down these barriers is a critical responsibility for any society that wishes to be guided by evidence and shared understanding. By strengthening every link in the chain—from the lab to our laws—we can build the bridge to a future shaped by insight and reason. If knowledge is power, how can we each help ensure it flows to where it’s needed most?
Climate
A Green Turn with Gaps: India’s Budget Backs Clean Tech but Skips Climate Adaptation
India’s Budget 2026–27 doesn’t shout climate ambition—but it hardwires it into clean manufacturing, carbon capture and energy supply chains, quietly reshaping the country’s green economy from the inside out.

India’s Union Budget 2026–27 may not carry a standalone climate chapter, but its green intent runs deep through the fine print. From carbon capture and battery storage to critical minerals and clean manufacturing, the budget signals a strategic shift: climate action is no longer framed as an environmental add-on, but as industrial policy and economic risk management rolled into one.
Presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on February 1, 2026, the budget places clean energy and climate-aligned manufacturing at the heart of India’s growth narrative. With a GDP growth target of around 7 percent and a sharp focus on fiscal discipline, sustainability is being embedded into supply chains, cities, transport and finance—quietly but deliberately.
Carbon Capture Takes Centre Stage
The most striking climate-linked announcement is the Rs 20,000 crore allocation over five years for Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS), aimed at hard-to-abate sectors such as power, steel, cement, refineries and chemicals. For the first time, industrial decarbonisation is being backed at scale through public finance, signalling recognition that renewables alone cannot carry India’s net-zero journey.
As Arunabha Ghosh of CEEW notes, the budget’s “prioritisation of carbon capture, utilisation and storage across power, steel, cement, refineries, and chemicals” places these sectors squarely at the centre of India’s long-term climate pathway. This marks a decisive move from aspiration to infrastructure.

Building the Clean Energy Ecosystem
The energy transition is supported by coordinated allocations across key ministries: Rs 32,915 crore for New and Renewable Energy, Rs 29,997 crore for Power, and Rs 24,124 crore for Atomic Energy. Customs duty exemptions have been extended to lithium-ion cells used in battery energy storage systems, inputs for solar glass manufacturing, and nuclear power project imports till 2035.
Aarti Khosla of Climate Trends captures this shift succinctly: “Coupled with the exemption given to battery manufacturing, VGF for BESS and grant to CCUS, the focus of the government is rightly tilting towards building an energy transition ecosystem.” She adds that continued reforms in power distribution could bring “360-degree improvement in India’s green energy supply chain.”
At the household level, the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana receives a major boost, reinforcing decentralised clean energy as a pillar of inclusive growth. Rooftop solar is increasingly being positioned not just as a climate solution, but as a competitiveness tool for small businesses and urban households.
Supply Chains, Not Just Solar Panels
Rather than headline-grabbing renewable capacity targets, Budget 2026–27 leans into industrial resilience. Duty exemptions for critical minerals processing equipment, solar glass inputs, and battery storage components underline a focus on domestic value addition.
Energy analyst Duttatreya Das of Ember observes that while there are “no big-ticket announcements for renewables,” the continued duty exemptions and manufacturing reforms are expected to “quietly strengthen clean energy supply chains.” This reflects a broader policy philosophy: competitiveness before capacity, foundations before scale.
Rare Earth Corridors and incentives for mineral-rich coastal states further indicate a push to secure upstream inputs essential for EVs, batteries, wind turbines and electronics—areas where geopolitical vulnerabilities are growing.
Clean Mobility and Greener Cities
Sustainability also shapes transport and urban planning. The budget proposes 20 new national waterways over five years, aims to double the share of inland and coastal shipping by 2047, and identifies seven high-speed rail corridors as environmentally sustainable growth connectors. Municipal finance incentives—such as Rs 100 crore support for cities issuing large bonds—open space for green urban infrastructure, including pollution control and climate-resilient services.
Labanya Prakash Jena,Director, Climate and Sustainability Initiative, highlights that such incentives can catalyse “green municipal bonds, particularly for pollution control and urban environmental projects,” linking fiscal reform directly with urban sustainability.
The Gaps That Remain
Despite these advances, the budget remains notably silent on climate adaptation. Heat stress, floods, water scarcity and climate-resilient agriculture receive no scaled-up fiscal roadmap. Vibhuti of IEEFA points out that while support for decentralised renewables and bioenergy has increased, spending on transmission and energy storage has stagnated or declined—areas that are “not optional but indispensable” for a high-renewables grid.
The absence of strong EV demand-pull measures and limited risk-sharing instruments for private capital also signal unfinished business in India’s clean transition.
A Budget of Signals, Not Slogans
Budget 2026–27 is not a climate manifesto. Instead, it is a signal budget—one that rewires incentives, de-risks clean manufacturing, and treats decarbonisation as an economic strategy rather than a moral appeal. Its strength lies in industrial tools and fiscal realism; its weakness, in adaptation and social resilience.
Whether this quiet green turn translates into measurable emissions reductions and climate resilience will depend on execution, state capacity, and private investment. But one thing is clear: India’s clean-tech transition has now entered the core of its economic planning.
-

 Society1 month ago
Society1 month agoThe Ten-Rupee Doctor Who Sparked a Health Revolution in Kerala’s Tribal Highlands
-

 COP303 months ago
COP303 months agoBrazil Cuts Emissions by 17% in 2024—Biggest Drop in 16 Years, Yet Paris Target Out of Reach
-

 Earth3 months ago
Earth3 months agoData Becomes the New Oil: IEA Says AI Boom Driving Global Power Demand
-

 COP303 months ago
COP303 months agoCorporate Capture: Fossil Fuel Lobbyists at COP30 Hit Record High, Outnumbering Delegates from Climate-Vulnerable Nations
-

 Society2 months ago
Society2 months agoFrom Qubits to Folk Puppetry: India’s Biggest Quantum Science Communication Conclave Wraps Up in Ahmedabad
-

 Women In Science4 months ago
Women In Science4 months agoThe Data Don’t Lie: Women Are Still Missing from Science — But Why?
-

 Space & Physics2 months ago
Space & Physics2 months agoIndian Physicists Win 2025 ICTP Prize for Breakthroughs in Quantum Many-Body Physics
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoAir Pollution Claimed 1.7 Million Indian Lives and 9.5% of GDP, Finds The Lancet






































