Health
Could LLMs Revolutionize Drug and Material Design?
These researchers have developed an innovative system that augments an LLM with graph-based AI models, designed specifically to handle molecular structures

A new method is changing the way we think about molecule design, bringing us closer to the possibility of using large language models (LLMs) to streamline the creation of new medicines and materials. Imagine asking, in plain language, for a molecule with specific properties, and receiving a comprehensive plan on how to synthesize it. This futuristic vision is now within reach, thanks to a collaboration between researchers from MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab.
A New era in molecular discovery
Traditionally, discovering the right molecules for medicines and materials has been a slow and resource-intensive process. It often involves the use of vast computational power and months of painstaking work to explore the nearly infinite pool of potential molecular candidates. However, this new method, blending LLMs with other machine-learning models known as graph-based models, offers a promising solution to speed up this process.
These researchers have developed an innovative system that augments an LLM with graph-based AI models, designed specifically to handle molecular structures. The approach allows users to input natural language queries specifying the desired molecular properties, and in return, the system provides not only a molecular design but also a step-by-step synthesis plan.
LLMs and graph models
LLMs like ChatGPT have revolutionized the way we interact with text, but they face challenges when it comes to molecular design. Molecules are graph structures—composed of atoms and bonds—which makes them fundamentally different from text. LLMs typically process text as a sequence of words, but molecules do not follow a linear structure. This discrepancy has made it difficult for LLMs to understand and predict molecular configurations in the same way they handle sentences.
To bridge this gap, MIT’s researchers created Llamole—a system that uses LLMs to interpret user queries and then switches between different graph-based AI modules to generate molecular structures, explain their rationale, and devise a synthesis strategy. The system combines the power of text, graphs, and synthesis steps into a unified workflow.
As a result, this multimodal approach drastically improves performance. Llamole was able to generate molecules that were far better at meeting user specifications and more likely to have a viable synthesis plan, increasing the success rate from 5 percent to 35 percent.
Llamole’s success lies in its unique ability to seamlessly combine language processing with graph-based molecular modeling. For example, if a user requests a molecule with specific traits—such as one that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and inhibit HIV—the LLM interprets the plain-language request and switches to a graph module to generate the appropriate molecular structure.
This switch occurs through the use of a new type of trigger token, allowing the LLM to activate specific modules as needed. The process unfolds in stages: the LLM first predicts the molecular structure, then uses a graph neural network to encode the structure, and finally, a retrosynthetic module predicts the necessary steps to synthesize the molecule. The seamless flow between these stages ensures that the LLM maintains an understanding of what each module does, further enhancing its predictive accuracy.
“The beauty of this is that everything the LLM generates before activating a particular module gets fed into that module itself. The module is learning to operate in a way that is consistent with what came before,” says Michael Sun, an MIT graduate student and co-author of the study.
Simplicity meets precision
One of the most striking aspects of this new method is its ability to generate simpler, more cost-effective molecular structures. In tests, Llamole outperformed other LLM-based methods and achieved a notable 35 percent success rate in retrosynthetic planning, up from a mere 5 percent with traditional approaches. “On their own, LLMs struggle to figure out how to synthesize molecules because it requires a lot of multistep planning. Our method can generate better molecular structures that are also easier to synthesize,” says Gang Liu, the study’s lead author.
By designing molecules with simpler structures and more accessible building blocks, Llamole could significantly reduce the time and cost involved in developing new compounds.
The road ahead
Though Llamole’s current capabilities are impressive, there is still work to be done. The researchers built two custom datasets to train Llamole, but these datasets focus on only 10 molecular properties. Moving forward, they hope to expand Llamole’s capabilities to design molecules based on a broader range of properties and improve the system’s retrosynthetic planning success rate.
In the long run, the team envisions Llamole serving as a foundation for broader applications beyond molecular design. “Llamole demonstrates the feasibility of using large language models as an interface to complex data beyond textual description, and we anticipate them to be a foundation that interacts with other AI algorithms to solve any graph problems,” says Jie Chen, a senior researcher at MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab.
With further refinements, Llamole could revolutionize fields from pharmaceuticals to material science, offering a glimpse into the future of AI-driven innovation in molecular discovery.
Health
Study Unveils Mucus Molecules That Block Salmonella and Prevent Diarrhea
A new MIT-led study reveals how key mucus molecules naturally shield the gut from dangerous bacteria like Salmonella
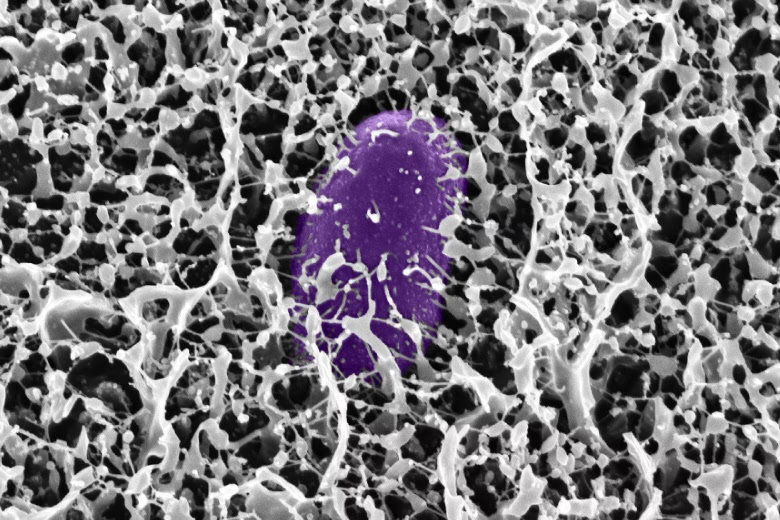
A new MIT-led study reveals how key mucus molecules naturally shield the gut from dangerous bacteria like Salmonella. The breakthrough opens new pathways for affordable, preventative treatments for travelers and soldiers at risk of infection.
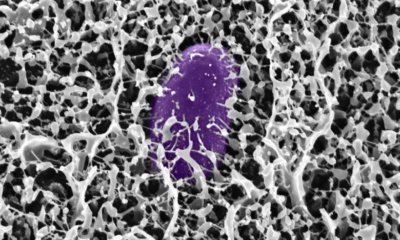
Researchers at MIT have discovered new powerful ways the body guards itself from dangerous bacteria: by deploying mucins, special molecules in mucus that neutralize microbes and stop infection before it starts. The team identified mucins—especially MUC2 and MUC5AC—in the digestive tract that shut down the genetic machinery Salmonella uses to invade cells and cause diarrhea.
“By using and reformatting this motif from the natural innate immune system, we hope to develop strategies to preventing diarrhea before it even starts. This approach could provide a low-cost solution to a major global health challenge that costs billions annually in lost productivity, health care expenses, and human suffering,” said Katharina Ribbeck, the Andrew and Erna Viterbi Professor of Biological Engineering at MIT, in a media statement.
In experiments, exposing Salmonella to the intestinal mucin MUC2 blocked the bacterial proteins that enable infection, turning off the critical regulator HilD. The study also found that a similar mucin from the stomach, MUC5AC, works the same way—and both molecules appear to protect against multiple foodborne germs triggered by similar genetic switches.
“We discovered that these mucins not only create a physical shield but also actively control whether pathogens can turn on genes needed for infection,” Ribbeck explained in the media statement.
Lead authors Kelsey Wheeler and Michaela Gold say synthetic versions of these mucins could soon be added to oral rehydration salts or chewable tablets, providing practical protection for troops, travelers, and people in high-risk areas. According to Wheeler, “Mucin mimics would particularly shine as preventatives, because that’s how the body evolved mucus — as part of this innate immune system to prevent infection,” she said.
Health
First Case of Rare and Deadly Fungus Identified in Sub-Saharan Africa
It is also the first time the rare and deadly fungal infection has been identified in an HIV-positive patient in the region

Doctors at the University of the Free State (UFS) and the National Health Laboratory Service (NHLS) at the Universitas Academic Hospital have confirmed the first recorded case of S. oblongispora mucormycosis in sub-Saharan Africa. It is also the first time the rare and deadly fungal infection has been identified in an HIV-positive patient in the region.
The case involved a 32-year-old man living with HIV who was admitted to Universitas Academic Hospital with severe swelling on the right side of his face. Despite being on antiretroviral therapy and treatment for hypertension, his condition worsened rapidly. Four days after admission, a CT scan and tissue biopsies were conducted. He died three days later, before a diagnosis could be confirmed.
Landmark discovery
Dr. Bonita van der Westhuizen, Senior Lecturer and Pathologist in the UFS Department of Medical Microbiology, described the discovery as a critical turning point for public health in the region.
“This discovery is significant because it highlights the presence of this fungal pathogen in a region where it may have been previously unrecognised or underreported. It now raises awareness about the diversity of fungal infections affecting immunocompromised populations and underscores the need for improved diagnostics, surveillance, and treatment strategies in the region,” she said in a media statement sent to EdPublica.
The case report, co-authored with Drs. Liska Budding and Christie Esterhuysen from the UFS/NHLS and Prof. Samantha Potgieter from the UFS Department of Internal Medicine, was published in Case Reports in Pathology last month.
Rapid and aggressive disease
Mucormycosis, caused by fungi from the order Mucorales, is known for its speed and severity. The infection can invade blood vessels, spread to vital organs, and resist the body’s immune defences.
“Mucorales fungi are known for their fast growth and ability to invade blood vessels. This allows the infection to spread quickly through the body, potentially reaching vital organs,” Dr. Van der Westhuizen explained in the statement. She added that external factors such as traumatic injuries or hospital-acquired infections can worsen the disease’s progression.
While mucormycosis usually strikes patients with underlying conditions like diabetes, cancer, or organ transplants, S. oblongispora has often been linked to infections in otherwise healthy individuals after traumatic inoculation. The lack of local data, however, means its prevalence in African populations remains unclear.
Diagnostic hurdles
In this case, invasive fungal infection was not initially suspected, and the patient did not receive antifungal medication or surgical treatment. The diagnosis was confirmed only after his death, highlighting the broader challenges of detecting fungal diseases in resource-limited settings.
“This is unfortunately the case with mould infections as most readily available diagnostic methods lack sensitivity and these pathogens take long to grow in the laboratory,” Dr. Van der Westhuizen said. “Fungal diagnostics is a specialised field that requires expertise. However, if clinicians are aware of these infections and they have an increased index of suspicion, appropriate therapy can be initiated even before the results are available.”
Experts warn that even with antifungal drugs and surgical removal of infected tissue, the window for treatment is narrow and survival rates remain low.
Building awareness and research
Dr. Van der Westhuizen is continuing her research on invasive mould infections as part of her PhD, focusing on fungal epidemiology and its impact on vulnerable groups such as HIV patients.
Her goal, she said in the media statement, is “to advance understanding and awareness of invasive mould infections, specifically S. oblongispora, in sub-Saharan Africa and among HIV patients. I aim to improve early diagnosis, treatment strategies, and clinical outcomes, as well as to highlight the importance of monitoring fungal infections in immunocompromised populations.”
She hopes the findings will spur more regional collaboration and investment in fungal diagnostics — an often overlooked but increasingly urgent frontier in infectious disease research.
Health
Giant Human Antibody Found to Act Like a Brace Against Bacterial Toxins
This synergistic bracing action gives IgM a unique advantage in neutralizing bacterial toxins that are exposed to mechanical forces inside the body
Our immune system’s largest antibody, IgM, has revealed a hidden superpower — it doesn’t just latch onto harmful microbes, it can also act like a brace, mechanically stabilizing bacterial toxins and stopping them from wreaking havoc inside our bodies.
A team of scientists from the S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS) in Kolkata, India, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), made this discovery in a recent study. The team reports that IgM can mechanically stiffen bacterial proteins, preventing them from unfolding or losing shape under physical stress.
“This changes the way we think about antibodies,” the researchers said in a media statement. “Traditionally, antibodies are seen as chemical keys that unlock and disable pathogens. But we show they can also serve as mechanical engineers, altering the physical properties of proteins to protect human cells.”
Unlocking a new antibody role
Our immune system produces many different antibodies, each with a distinct function. IgM, the largest and one of the very first antibodies generated when our body detects an infection, has long been recognized for its front-line defense role. But until now, little was known about its ability to physically stabilize dangerous bacterial proteins.
The SNBNCBS study focused on Protein L, a molecule produced by Finegoldia magna. This bacterium is generally harmless but can become pathogenic in certain situations. Protein L acts as a “superantigen,” binding to parts of antibodies in unusual ways and interfering with immune responses.
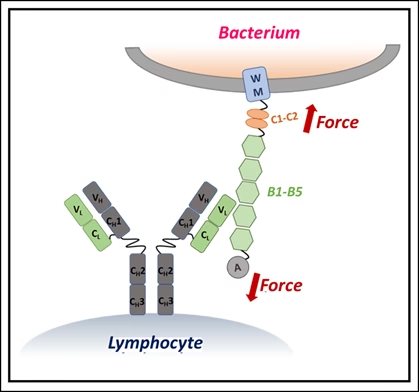
Using single-molecule force spectroscopy — a high-precision method that applies minuscule forces to individual molecules — the researchers discovered that when IgM binds Protein L, the bacterial protein becomes more resistant to mechanical stress. In effect, IgM braces the molecule, preventing it from unfolding under physiological forces, such as those exerted by blood flow or immune cell pressure.
Why size matters
The stabilizing effect depended on IgM concentration: more IgM meant stronger resistance. Simulations showed that this is because IgM’s large structure carries multiple binding sites, allowing it to clamp onto Protein L at several locations simultaneously. Smaller antibodies lack this kind of stabilizing network.
“This synergistic bracing action gives IgM a unique advantage in neutralizing bacterial toxins that are exposed to mechanical forces inside the body,” the researchers explained.
The finding highlights an overlooked dimension of how our immune system works — antibodies don’t merely bind chemically but can also act as mechanical modulators, physically disarming toxins.
Such insights could open a new frontier in drug development, where future therapies may involve engineering antibodies to stiffen harmful proteins, effectively locking them in a harmless state.
The study suggests that by harnessing this natural bracing mechanism, scientists may be able to design innovative treatments that go beyond traditional antibody functions.
-

 Space & Physics5 months ago
Space & Physics5 months agoIs Time Travel Possible? Exploring the Science Behind the Concept
-

 Earth6 months ago
Earth6 months ago122 Forests, 3.2 Million Trees: How One Man Built the World’s Largest Miyawaki Forest
-

 Space & Physics6 months ago
Space & Physics6 months agoDid JWST detect “signs of life” in an alien planet?
-

 Know The Scientist5 months ago
Know The Scientist5 months agoNarlikar – the rare Indian scientist who penned short stories
-

 Society4 months ago
Society4 months agoShukla is now India’s first astronaut in decades to visit outer space
-

 Society4 months ago
Society4 months agoAxiom-4 will see an Indian astronaut depart for outer space after 41 years
-

 Earth4 months ago
Earth4 months agoWorld Environment Day 2025: “Beating plastic pollution”
-

 Society6 months ago
Society6 months agoRabies, Bites, and Policy Gaps: One Woman’s Humane Fight for Kerala’s Stray Dogs