Space & Physics
Need of the Hour – Evading the Kessler Syndrome
In 1978, Donald J. Kessler, an astrophysicist, predicted collisions between satellites can get out of hand as their population keeps increasing.

In 2009, the Iridium 33 and Kosmos 2251 satellites collided to produce as many as 2,000 debris fragments, spraying 10 cm wide pieces in every direction – at speeds faster than a bullet.
If any of these ever struck the ISS, orbiting closely, then all hell can break loose! Remember that scene in Gravity (2013) when Sandra Bullock’s character gets flung around? Well, it’s just one of several worse-case scenarios.
Even today, these space debris hover there, too close to be completely risk-free to the ISS.
The US’ operate a Space Surveillance Network that tracks these debris, along with more than 20,000 fragments. They comprise old rocket booster stages, junk satellites, missile components from anti-satellite launches.
However, very tiny pieces of fragments (<10 cm) can still be missed by ground radars. Space debris can include spent rocket stages, or defunct satellites drifting in space.
And a technical fix in orbital debris removing technology arose.
Last month February 18th saw the launch of the Active Debris Removal by Astroscale-Japan (or ADRAS-J) satellite from Rocket Lab’s launch station in New Zealand. ADRAS-J is yet to actually demonstrate debris removal, as it’s parked in a rendezvous orbit in preparation for the demonstration later this month.
In 2022, the UK stated Active Debris Removal (ADR) as being vital to their Plan for Space Sustainability to “become tomorrow’s norms in space operation”.
Space agencies across the world now issue commands for ‘collision avoidance maneuvers’ (CAM) when satellites cross within a certain radius.
In fact, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) actually made public a trend showing the number of CAM commands issued rising every year. Such close-calls will only increase with the cumulative increase of satellites in orbit.
Here’s a plot from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) 2022 Space Environment Report.
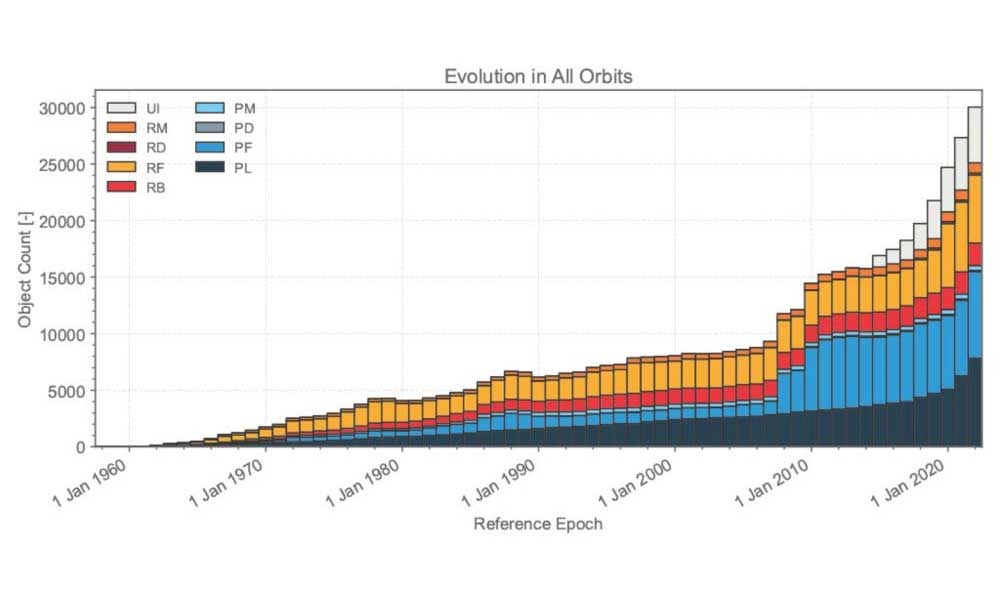
A plot of the number of space debris against time. The legend indicates the various types of space debris (rocket, satellite parts etc.). Credit: ESA
But the problem is that – these satellite numbers are rising exponentially in such a short time – with mega-constellations entering center stage.
SpaceX launched the Starlink initiative, to demonstrate connectivity even in the remotest parts of the world.
However, they alone have 5,504 satellites out there to date, all at low-earth orbit – under 600 km, which is quite where the crowd of satellites are now. That’s about 58% of the 9,414 operational satellites out there. And this happened metaphorically overnight – in the past few years. SpaceX plans to operate some 42,000 satellites in a decade.
The fear is that unregulated growth of satellites – or even satellite litter that are defunct – can make what is known as the Kessler syndrome, a reality.
When Donald Kessler anticipated a chain reaction …
In 1978, Donald J. Kessler, an astrophysicist, predicted that collisions between satellites can trigger a domino effect of other satellite collisions above a certain threshold. Dubbed the Kessler syndrome, it’s a worst-case scenario possible in outer space, when earth’s orbit becomes impossible to thrive in or operate from.
To partly address the growing clutter of low-earth orbit satellites, the US’ Federal Communications Council (FCC) has put up legislation to have newly launched satellites deorbit 5 years after operations.
The irony is that the Kessler syndrome was foreseeable, except it was ignored by policymakers until they simply couldn’t.

Scientists building a satellite at RAL Space. Credit: UK STFC / Wikimedia
Western countries have taken some onus of responsibility into these space sustainability initiatives, simply because countries like the US own most of the satellite infrastructure operating in orbit.
From space shuttles, rockets, space planes and the lunar lander that brought Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin to the moon, the Space Age heralded a brand new era for space technologies and research. But no space technology probably had more societal impact than the satellite.
Seen vital for development and infrastructure, satellites are now ubiquitous, manufactured not just by space agencies, but also by engineering labs in universities, private companies and start-ups across the world.
However, our costly endeavor to improve human lives are breeding new problems. And as a last resort, engineers are at it again to come up with technical fixes.
But weren’t the technical risks understood if Kessler expressed his concern in the 1970s?
Satellites, just like any technology, come with its set of benefits and risks. The benefits of satellites are obvious to many – phone connections, weather forecasting, banking, studying climate change, and the list goes on.
At the end of a satellite’s lifespan though, many just stay there, as defunct satellites.
Sure, there’s a ‘graveyard’ orbit where satellites can be made defunct after pushing them to a higher orbit to lay to rest forever. But not every defunct satellite is. In fact, 60% of all satellites are defunct. The operational satellites constitute a tiny minority.
Partly to do with this mess is a lack of priority. The Space Race played out during the peak of the Cold War when both the US and Soviets wanted to demonstrate technological superiority.
However, the outer orbit isn’t just a matter of mediating traffic or cleaning debris either.
Space militarization has raised fears. Much of the initial Space Race began with the US and Soviets fearing the other could surveil over their national boundaries. But the tensions have now made headlines, with the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine, with the US alleging that the Russians are developing a satellite that can drop nuclear weapons against the West. Building such a weapon would be violative of the 1967 Outer Space Treaty, in addition to several other regulations against weapons of mass destruction (WMDs).
There’s also anti-satellite launch systems firing repurposed ballistic missiles into space missiles. The US, Russia, China and India all possess this technology – and have the capacity to threaten orbital infrastructure – civilian or military. But the consequence of losing control over the weapons, is to hit the threshold dictated by the Kessler syndrome.
We’ll need to bear in mind that even technical fixes can’t fix design thinking. When planners aren’t held accountable, for their individual decisions – such avoidable doomsday disasters become a talking point.
Space & Physics
MIT Pioneers Real-Time Observation of Unconventional Superconductivity in Magic-Angle Graphene
Physicists have directly observed unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle twisted tri-layer graphene using a new experimental platform, revealing a unique pairing mechanism
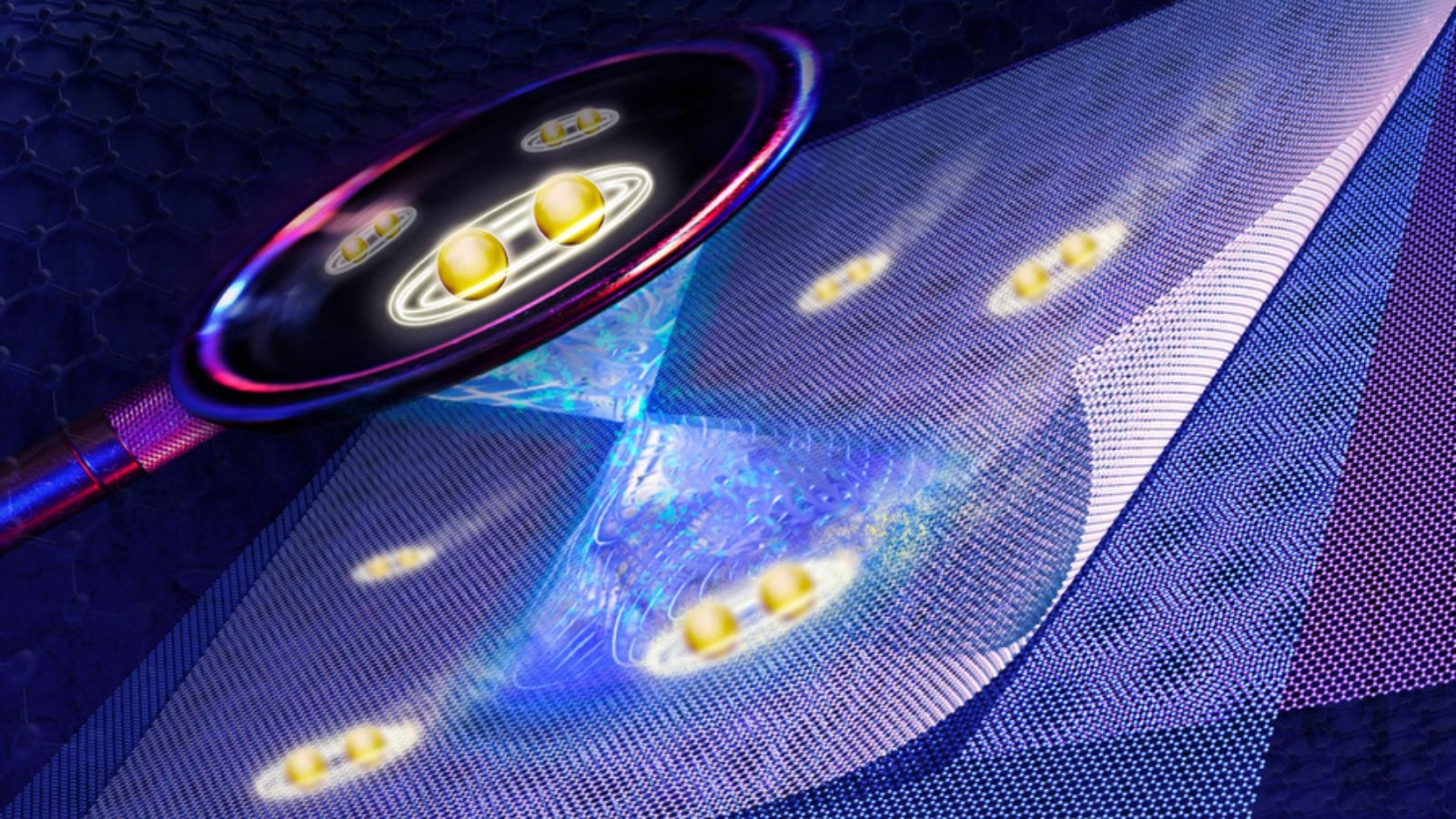
MIT physicists have unveiled compelling direct evidence for unconventional superconductivity in “magic-angle” twisted tri-layer graphene—an atomically engineered material that could reimagine the future of energy transport and quantum technologies. Their new experiment marks a pivotal step forward, offering a fresh perspective on how electrons synchronize in precisely stacked two-dimensional materials, potentially laying the groundwork for next-generation superconductors that function well above current temperature limits.
Instead of looking merely at theoretical possibilities, the MIT team built a novel platform that lets researchers visualize the superconducting gap “as it emerges in real-time within 2D materials,” said co-lead author Shuwen Sun in a media statement. This gap is crucial, reflecting how robust the material’s superconducting state is during temperature changes—a key indicator for practical applications.
What’s striking, said Jeong Min Park, study co-lead author, is that the superconducting gap in magic-angle graphene differs starkly from the smooth, uniform profile seen in conventional superconductors. “We observed a V-shaped gap that reveals an entirely new pairing mechanism—possibly driven by the electrons themselves, rather than crystal vibrations,” Park said. Such direct measurement is a “first” for the field, giving scientists a more refined tool for identifying and understanding unconventional superconductivity.
Senior author Pablo Jarillo-Herrero emphasized that their method could help crack the code behind room-temperature superconductors: “This breakthrough may trigger deeper insights not just for graphene, but for the entire class of twistronic materials. Imagine grids and quantum computers that operate with zero energy loss—this is the holy grail we’re moving toward,” Jarillo-Herrero said in the MIT release.
Collaborators included scientists from Japan’s National Institute for Materials Science, broadening the impact of the research. The discovery builds on years of progress since the first magic-angle graphene experiments in 2018, opening what many now call the “twistronics” era—a field driven by stacking and twisting atom-thin materials to unlock uniquely quantum properties.
Looking ahead, the team plans to expand its analysis to other ultra-thin structures, hoping to map out electronic behavior not only for superconductors, but for a wider range of correlated quantum phases. “We can now directly observe electron pairs compete and coexist with other quantum states—this could allow us to design new materials from the ground up,” said Park in her public statement.
The research underscores the value of visualization in fundamental physics, suggesting that direct observation may be the missing link to controlling quantum phenomena for efficient, room-temperature technology.
Space & Physics
Atoms Speak Out: Physicists Use Electrons as Messengers to Unlock Secrets of the Nucleus
Physicists at MIT have devised a table-top method to peer inside an atom’s nucleus using the atom’s own electrons

Physicists at MIT have developed a pioneering method to look inside an atom’s nucleus — using the atom’s own electrons as tiny messengers within molecules rather than massive particle accelerators.
In a study published in science, the researchers demonstrated this approach using molecules of radium monofluoride, which pair a radioactive radium atom with a fluoride atom. The molecules act like miniature laboratories where electrons naturally experience extremely strong electric fields. Under these conditions, some electrons briefly penetrate the radium nucleus, interacting directly with protons and neutrons inside. This rare intrusion leaves behind a measurable energy shift, allowing scientists to infer details about the nucleus’ internal structure.
The team observed that these energy shifts, though minute — about one millionth of the energy of a laser photon — provide unambiguous evidence of interactions occurring inside the nucleus rather than outside it. “We now have proof that we can sample inside the nucleus,” said Ronald Fernando Garcia Ruiz, the Thomas A. Franck Associate Professor of Physics at MIT, in a statement. “It’s like being able to measure a battery’s electric field. People can measure its field outside, but to measure inside the battery is far more challenging. And that’s what we can do now.”
Traditionally, exploring nuclear interiors required kilometer-long particle accelerators to smash high-speed beams of electrons into targets. The MIT technique, by contrast, achieves similar insight with a table-top molecular setup. It makes use of the molecule’s natural electric environment to magnify these subtle interactions.
The radium nucleus, unlike most which are spherical, has an asymmetric “pear” shape that makes it a powerful system for studying violations of fundamental physical symmetries — phenomena that could help explain why the universe contains far more matter than antimatter. “The radium nucleus is predicted to be an amplifier of this symmetry breaking, because its nucleus is asymmetric in charge and mass, which is quite unusual,” Garcia Ruiz explained.
To conduct their experiments, the researchers produced radium monofluoride molecules at CERN’s Collinear Resonance Ionization Spectroscopy (CRIS) facility, trapped and cooled them in laser-guided chambers, and then measured laser-induced energy transitions with extreme precision. The work involved MIT physicists Shane Wilkins, Silviu-Marian Udrescu, and Alex Brinson, alongside international collaborators.
“Radium is naturally radioactive, with a short lifetime, and we can currently only produce radium monofluoride molecules in tiny quantities,” said Wilkins. “We therefore need incredibly sensitive techniques to be able to measure them.”
As Udrescu added, “When you put this radioactive atom inside of a molecule, the internal electric field that its electrons experience is orders of magnitude larger compared to the fields we can produce and apply in a lab. In a way, the molecule acts like a giant particle collider and gives us a better chance to probe the radium’s nucleus.”
Going forward, the MIT team aims to cool and align these molecules so that the orientation of their pear-shaped nuclei can be controlled for even more detailed mapping. “Radium-containing molecules are predicted to be exceptionally sensitive systems in which to search for violations of the fundamental symmetries of nature,” Garcia Ruiz said. “We now have a way to carry out that search”
Space & Physics
Physicists Double Precision of Optical Atomic Clocks with New Laser Technique
MIT researchers develop a quantum-enhanced method that doubles the precision and stability of optical atomic clocks, paving the way for portable, ultra-accurate timekeeping.
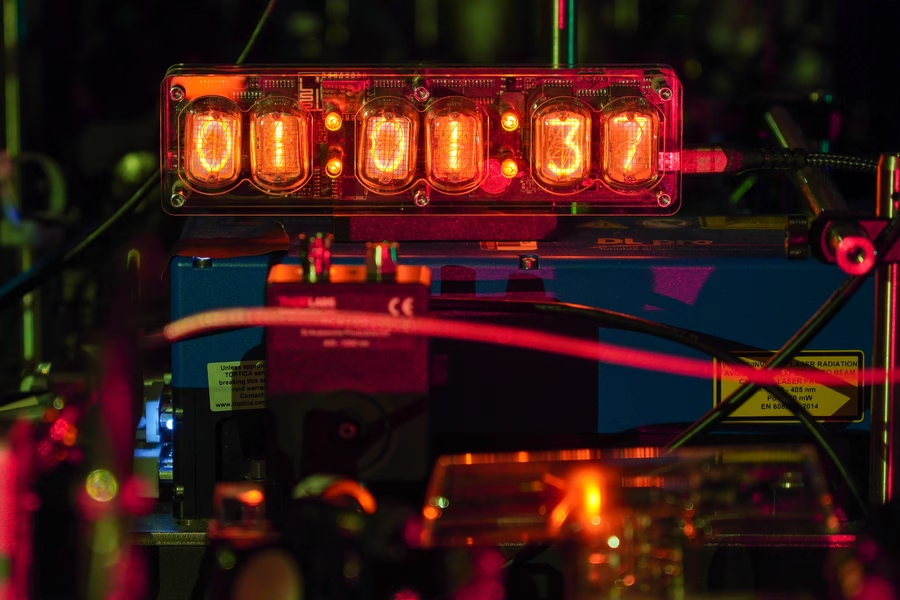
MIT physicists have unveiled a new technique that could significantly improve the precision and stability of next-generation optical atomic clocks, devices that underpin everything from mobile transactions to navigation apps. In a recent media statement, the MIT team explained: “Every time you check the time on your phone, make an online transaction, or use a navigation app, you are depending on the precision of atomic clocks. An atomic clock keeps time by relying on the ‘ticks’ of atoms as they naturally oscillate at rock-steady frequencies.”
Current atomic clocks rely on cesium atoms tracked with lasers at microwave frequencies, but scientists are advancing to clocks based on faster-ticking atoms like ytterbium, which can be tracked with lasers at higher, optical frequencies and discern intervals up to 100 trillion times per second.
A research group at MIT, led by Vladan Vuletić, the Lester Wolfe Professor of Physics, detailed that their newly developed method harnesses a laser-induced “global phase” in ytterbium atoms and boosts this effect using quantum amplification. Vuletić stated, “We think our method can help make these clocks transportable and deployable to where they’re needed.” The approach, called global phase spectroscopy, doubles the precision of an optical atomic clock, enabling it to resolve twice as many ticks per second compared to standard setups, and promises further gains with increasing atom counts.
The technique could pave the way for portable optical atomic clocks able to measure all manner of phenomena in various locations. Vuletić summarized the broader scientific ambitions: “With these clocks, people are trying to detect dark matter and dark energy, and test whether there really are just four fundamental forces, and even to see if these clocks can predict earthquakes.”
The MIT team has previously demonstrated improved clock precision by quantumly entangling hundreds of ytterbium atoms and using time reversal tricks to amplify their signals. Their latest advance applies these methods to much faster optical frequencies, where stabilizing the clock laser has always been a major challenge. “When you have atoms that tick 100 trillion times per second, that’s 10,000 times faster than the frequency of microwaves,” said Vuletić in the statement. Their experiments revealed a surprisingly useful “global phase” information about the laser frequency, previously thought irrelevant, unlocking the potential for even greater accuracy.
The research, led by Vuletić and joined by Leon Zaporski, Qi Liu, Gustavo Velez, Matthew Radzihovsky, Zeyang Li, Simone Colombo, and Edwin Pedrozo-Peñafiel of the MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms, was published in Nature. They believe the technical benefits of the new method will make atomic clocks easier to run and enable stable, transportable clocks fit for future scientific exploration, including earthquake prediction, fundamental physics, and global time standards.
-

 Space & Physics6 months ago
Space & Physics6 months agoIs Time Travel Possible? Exploring the Science Behind the Concept
-

 Know The Scientist6 months ago
Know The Scientist6 months agoNarlikar – the rare Indian scientist who penned short stories
-

 Know The Scientist5 months ago
Know The Scientist5 months agoRemembering S.N. Bose, the underrated maestro in quantum physics
-

 Space & Physics3 months ago
Space & Physics3 months agoJoint NASA-ISRO radar satellite is the most powerful built to date
-

 Society5 months ago
Society5 months agoAxiom-4 will see an Indian astronaut depart for outer space after 41 years
-

 Society5 months ago
Society5 months agoShukla is now India’s first astronaut in decades to visit outer space
-

 Society5 months ago
Society5 months agoWhy the Arts Matter As Much As Science or Math
-

 Earth5 months ago
Earth5 months agoWorld Environment Day 2025: “Beating plastic pollution”























